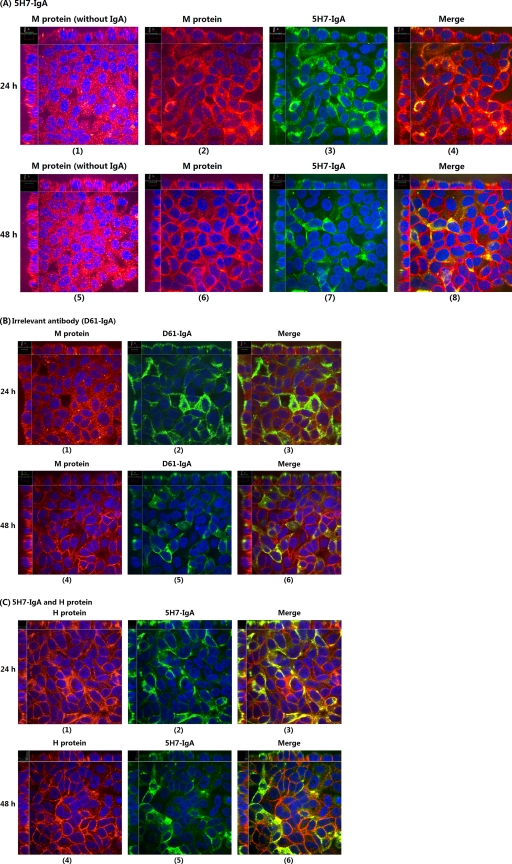
Fig. 4.
Confocal microscopic images from two-color immunofluorescent staining of M protein and IgA antibody. The polarized Vero-IgR cell monolayers grown on polyester membranes were either infected with measles virus at an MOI of 1 or mock infected via the apical surfaces. Two hours later, 20 μg of 5H7-IgA or irrelevant anti-HIV gp41 IgA MAb was added to the basal chambers. At 24 or 48 h after initial infection, the membrane-attached cells were fixed, permeabilized, and stained with Alexa Fluor (R) 555 goat anti-mouse IgG to detect M protein (or H protein) and FITC-conjugated goat anti-mouse IgA to detect IgA antibodies. (A) Staining of M protein and 5H7-IgA at 24 h (1 to 4) and 48 h (5 to 8) showing significant colocalization of M and 5H7-IgA. (B) Staining of M protein and anti-HIVgp41-IgA (D61-IgA) at 24 h (1 to 3) and 48 h (4 to 6) showing no colocalization of M and irrelevant IgA. (C) Staining of H protein and 5H7-IgA at 24 h (1 to 3) and 48 h (4 to 6) showing no colocalization of H and 5H7-IgA.