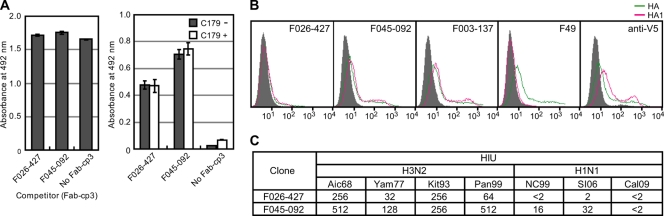
Fig. 4.
F045-092 and F026-427 recognize HA1 and show HI activities. (A) Competition for binding to HA in ELISA between C179 and F045-092 or F026-427. Formalin-inactivated New Caledonia/99 virus particles were coated onto an immunoplate. (Left) A total of 50 μl of 0.5 μg/ml of C179 was mixed with 50 μl of 2 μg/ml of Fab-cp3 of F026-427, F045-092, or PBS (No Fab-cp3) and applied to the immunoplate. Bound C179 was detected with anti-mouse IgG-HRP. (Right) A total of 50 μl of 0.5 μg/ml of Fab-cp3 of F026-427, F045-092, or PBS (No Fab-cp3) was mixed with 50 μl of 2 μg/ml of C179 (C179+) or with 50 μl PBS (C179−) and applied to the immunoplate. The bound Fab-cp3 was detected with rabbit anti-cp3 polyclonal antibody followed by anti-rabbit IgG-HRP. Values are the averages of duplicate experiments, and the standard deviation is depicted by an error bar. (B) FCM analyses of the cells expressing HA and HA1 of Aichi/68 virus. FCM signals for mock transfection (gray-filled area), HA-expressing cells (green), and HA1-expressing cells (pink) are shown. F49 Ab binds to an epitope on HA2 that is commonly present on all H3 subtype viruses (26). Anti-V5 Ab binds to the V5 tag located at the membrane-proximal end of HA. F003-137 binds to the B2/D site located on the globular head of HA (17). (C) HI activity of IgG from F045-092 and F026-427 against H3N2 (Aichi/68, Yamanashi/77, Kitakyushu/93, Panama/99) and H1N1 (New Caledonia/99, Solomon Islands/2006, California/2009 pdm) viruses.