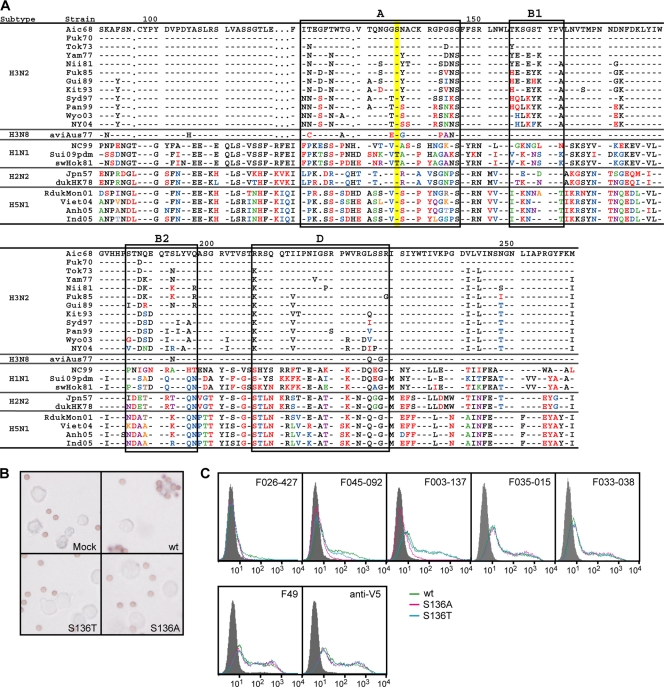
Fig. 6.
Effect of one amino acid substitution at residue 136 of HA on the binding activity of F045-092 and F026-427. (A) Amino acid sequences of HA1 of various strains. The sequence of the Aichi/68 H3N2 virus strain was used as a standard for comparison. The bars indicate the same amino acid as in the standard. Amino acids that differ from those of the standard are indicated by using a different color. Amino acid sequences in sites A, B1, B2, and D are boxed. The amino acids at residue 136 are shaded in yellow. (B) Attachment of reticulocytes to cells expressing wild-type (wt) HA or two variant HAs of the Aichi/68 H3N2 influenza strain with amino acid substitutions at residue 136. (C) Reactivity of F045-092 and F026-427 with mutant HAs of Aichi/68 on 293T cells. FCM signals for mock transfection (gray-filled area), Aic68 wild type (green), and two kinds of mutants, Aic68/S136A (pink) and Aic68/S136T (blue), are shown. Ser136 of the wild type was changed to alanine and threonine in Aic68/S136A and Aic68/S136T, respectively. While positive-control antibody, anti-V5 antibody, F49, F035-015, and F033-038 reacted with both the wild type and the mutants to the same extent, F045-092 and F026-427 reacted with the mutants more weakly than the wild type.