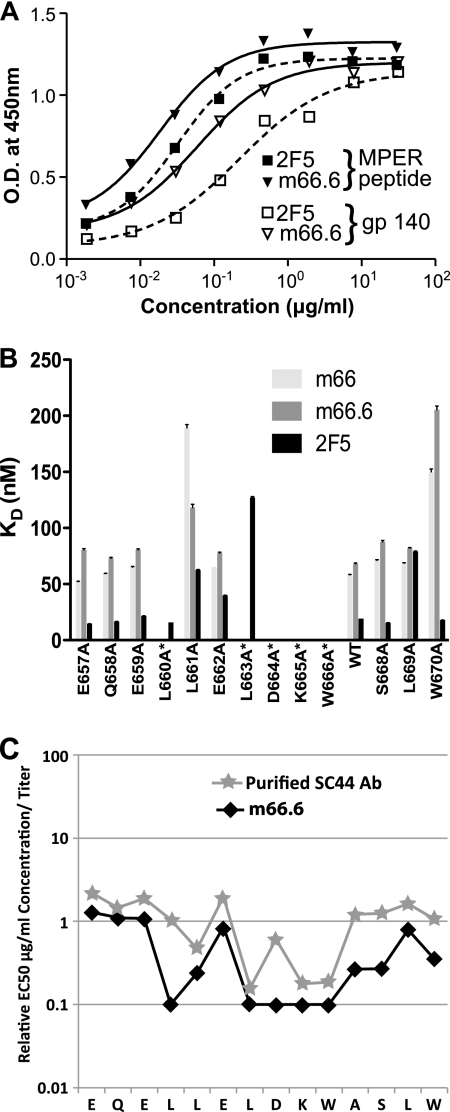
Fig. 3.
Reactivity profiles of IgG1 m66.6 and IgG1 m66. (A) Similar binding of m66.6 and 2F5 to the membrane-proximal external region (MPER) peptide SP62 and gp140-JRFL as measured by ELISA. O.D., optical density. (B) Epitope mapping of IgGs m66, m66.6, and 2F5 through alanine-scanning mutagenesis. Surface plasmon resonance (SPR) was used to determine the binding affinities of alanine-scanning mutant peptides of the gp41 MPER (residues 657 to 670) to IgG1 m66, IgG1 m66.6, and IgG1 2F5; a mutant of the Ala670 position was not included. The equilibrium dissociation constants (KDs) of the Abs for each of the alanine replacement mutations for m66, m66.6, and 2F5 described are shown. For cases in which peptide binding was too weak for the SPR profiles to produce a proper fit (see Fig. S3 in the supplemental material), a KD of zero is reported. WT, wild type. (C) Epitope mapping of Ab from plasma from patient SC44 that was affinity purified on MPER peptide; the purified Ab was directly compared to m66.6 using an alanine-scanning mutant HIV-1 multiplex binding assay. The titers of both Abs on the alanine-scanning mutants were determined, and the EC50 was calculated for each mutant peptide. Relative binding values are plotted from the EC50 for each peptide bearing an Ala substitution within the m66.6 epitope divided by the binding values for peptides bearing Ala substitutions outside the m66.6 epitope. Binding by m66.6 and the purified SC44 Ab depended upon Leu residues preceding the DKW core binding motif.