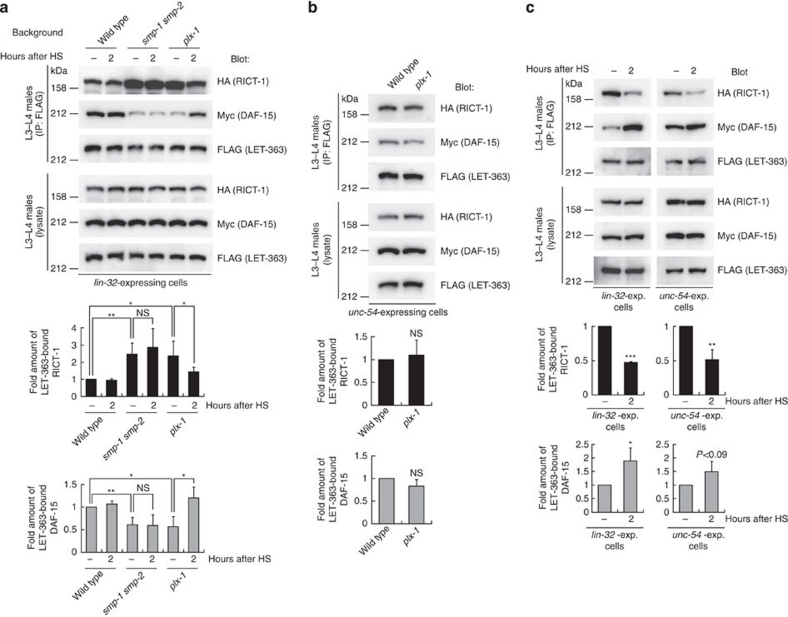
Figure 4. The SMP signal promotes a shift of the LET-363-associated adaptor from RICT-1 towards DAF-15.
(a) TORC1 and TORC2 formations in wild-type, plx-1 and smp-1 smp-2 mutant ray precursor cells. Transgenic L3–L4 males (ncEx9005) in the indicated genetic backgrounds, which carry three TORC component genes under the lin-32p together with plx-1 under hsp (hsp∷plx-1), were either untreated (−) or treated with brief heat-shock and collected two hours after heat-shock (2). FLAG∷LET-363 proteins in the lysate were immunoprecipitated, followed by analysis of IP and lysates. The intensity of co-immunoprecipitated HA∷RICT-1 (black bars) or Myc∷DAF-15 (grey bars) normalized by FLAG∷LET-363 in IP is shown in the graphs. Shown are the means±s.e.m. of four independent experiments. (b) TORC1 and TORC2 formations in unc-54-expressing muscle cells in wild-type and plx-1 mutants, which were analysed with a line, ncEx9007. The intensity of co-immunoprecipitated HA∷RICT-1 (black bars) or Myc∷DAF-15 (grey bars) normalized by FLAG∷LET-363 in IP is shown in the graphs. Shown in the graphs are the means±s.e.m. of four independent experiments. (c) TORC1 and TORC2 formations under reinforced SMP signalling. The same protocol was employed as in a, except for that the lines carry both hsp∷smp-1 and hsp∷plx-1 transgenes. ncEx9011 was utilized to analyse the TORC formations in lin-32-expressing cells; ncEx9012, in unc-54-expressing cells. The intensity of co-immunoprecipitated HA∷RICT-1 (black bars) or Myc∷DAF-15 (grey bars) normalized by FLAG∷LET-363 in IP is shown in the graphs. Shown in the graphs are the means±s.e.m. of three independent experiments. One asterisk indicates P<0.05; two asterisks, P<0.005; three asterisks, P<0.001 for all panels. Paired t-test was carried out to calculate the P-values. NS, not significant (P>0.05).