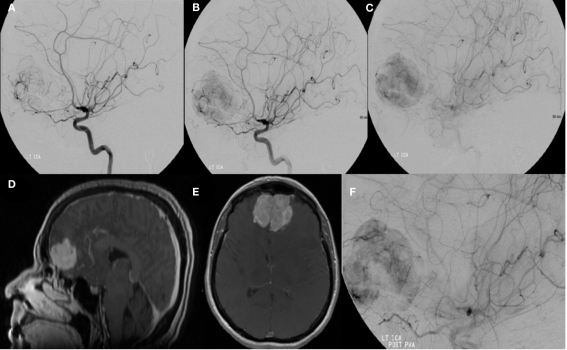
Figure 4.
A left internal carotid artery injection demonstrates a highly vascular mass in the region of the anterior cranial fossa predominantly supplied by dural branches from the left ophthalmic artery and branches of the anterior cerebral artery and characteristics consistent with a hemangiopericytoma (A–C). Tumor supply involves relatively few larger vessels with extensive penetration by small branching vessels. Magnetic resonance imaging with contrast shows an enhancing, dural-based, bifrontal mass in the anterior cranial fossa (D,E). The origin of vessel supply from the ophthalmic arteries limited the ability to safely embolize the tumor. Partial pre-operative devascularization was achieved with 45–150 and 150–250 μm PVA particles injected into distal left ophthalmic artery branches supplying the tumor (F). Pathology confirmed hemangiopericytoma.