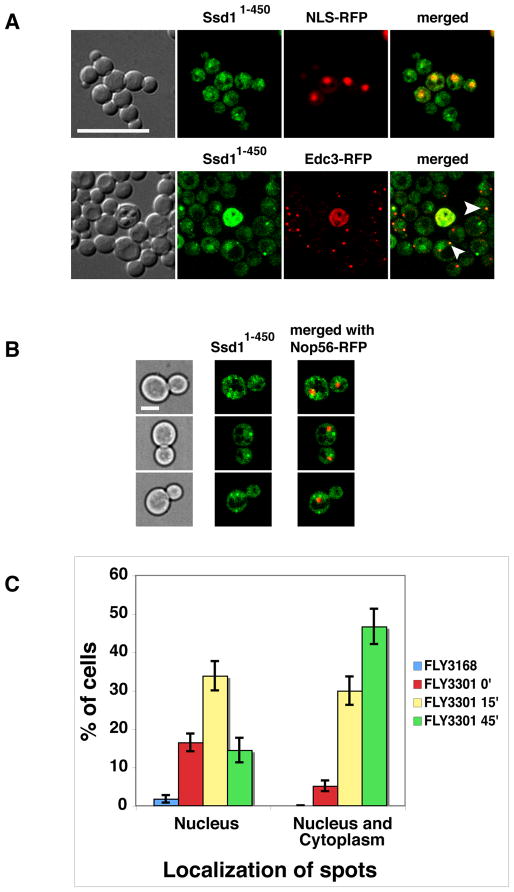
Figure 7. Nuclear and cytoplasmic Ssd11–450 is aberrant in cbk1 mutants.
A) The localization of physiologically expressed Ssd11–450-GFP was monitored in cbk1Δ cells (FLY3202) co-expressing an RFP-tagged nuclear marker (NLS-RFP, pKW1219) or P-body protein (Edc3-RFP, pRP1574). Ssd11–450-GFP accumulates in nuclei in cbk1Δ cells to the same extent as it does in CBK1 cells (compare to Fig. 2). In addition, Ssd11–450 localizes to a few nuclear and cytoplasmic puncta in cbk1Δ cells. Approximately half of the Ssd11–450 cytoplasmic puncta colocalize with Edc3 (see arrowheads). B) Physiologically expressed Ssd11–450-GFP was monitored in analog-sensitive cbk1-as mutants that express the nucleolar marker Nop56-RFP (FLY3301). Micrographs were taken 25 min after addition of the Cbk1-as inhibitor 1NA-PP1. C) Graphical representation of the cbk1-as data. Upon Cbk1 inhibition, the number of cells with nuclear and cytoplasmic Ssd11–450-GFP puncta increases over time. In the absence of 1NA-PP1, cbk1-as cells exhibit enhanced level of nuclear puncta compared to corresponding CBK1+ cells (FLY3168). The cells were monitored by spinning disk fluorescence microscopy and all images represent single optical sections. Scale bars = 8 um (A) and 4 um (B).