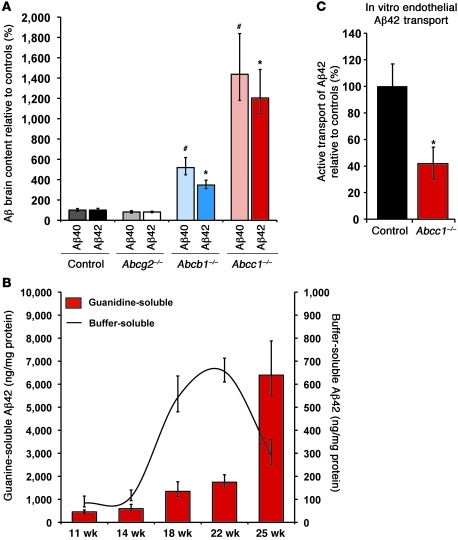
Figure 2. Deficiency of ABCC1 promotes the accumulation of Aβ.
(A) At age 25 weeks, ABCC1 deficiency leads to a marked increase in insoluble Aβ as measured by ELISA. n ≥ 4. #P < 0.05 versus Aβ40; *P < 0.05 versus Aβ42. (B) Buffer-soluble Aβ42 is precipitously reduced at age 25 weeks versus 22 weeks (–56%), possibly due to its deposition into insoluble deposits within the brain. At this same age, the area occupied by Aβ deposits measured by immunohistochemistry is elevated by 83% (Supplemental Figure 1). Error bars show SEM. n ≥ 5. (C) Transport of Aβ42 from the abluminal (brain) into the luminal (blood) compartment is impaired in Abcc1–/– endothelia. The mean Aβ42 transport rate of Abcc1–/– cells during the first 6 hours after addition of Aβ42 peptides was only 40% of control cells. Error bars show SEM. n = 3.