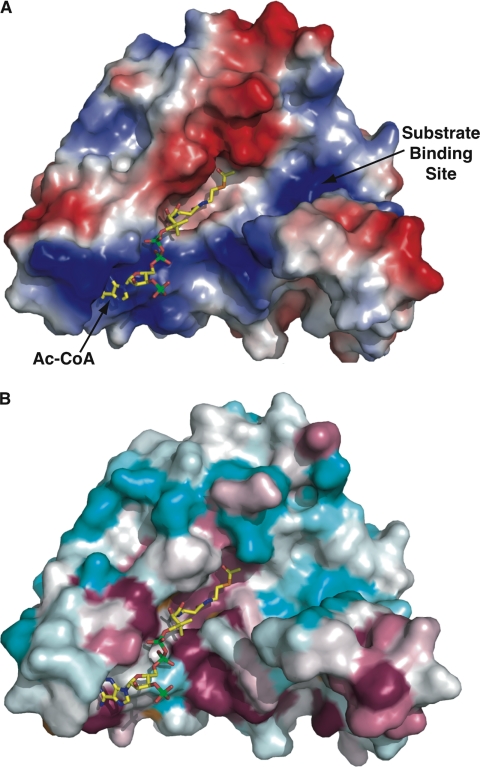
FIGURE 7.
FrbF pockets define the substrate- and acyl donor-binding sites. A, surface representation of the FrbF monomer with a vacuum electrostatic potential superimposed. The coordinates of acetyl-CoA are shown as yellow sticks. The acyl donor binds in a deep groove running along the width of the enzyme. A second pocket is located adjacent to the acyl group, and basic residues in this pocket may help stabilize the anionic diphosphates in the substrate conjugate. B, the same view of the FrbF surface but superimposed is a colored-coded representation of the sequence conservation shown as a gradient from cyan (least conserved) to pink (most conserved). Residues that line the acetyl-CoA-binding site and active site are conserved, as would be expected. Notice that residues in the putative substrate-binding pocket are less conserved, consistent with the range of substrates (such as aminoglycosides) that are accommodated by other members of this enzyme family.