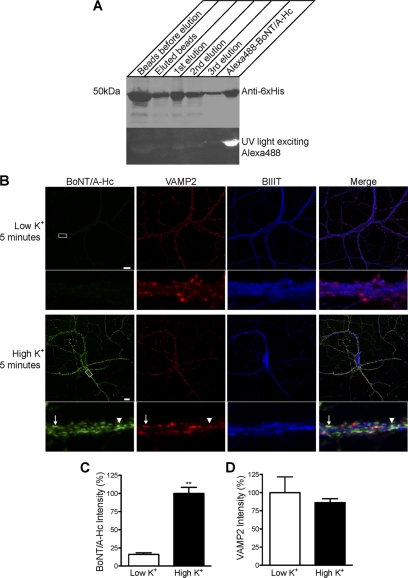
FIGURE 1.
The uptake of Alexa Fluor 488-BoNT/A-Hc in cultured hippocampal neurons is activity-dependent. A, Western blot of BoNT/A-Hc. Recombinant BoNT/A-Hc was expressed and purified on Co2+-IDA agarose before conjugation to Alexa Fluor 488 C5 maleimide. The fractions (of equivalent volume, 6 μl) indicated on the figure were run on an SDS-PAGE, and Western blotting using a His6 antibody was carried out to confirm the presence of the protein. The PVDF membrane was exposed to UV light to check the conjugation of the protein. B, cultured hippocampal neurons incubated for 5 min with Alexa Fluor 488-BoNT/A-Hc (100 nm) in the absence or presence of high K+. Neurons were then fixed and processed for βIII-tubulin (BIIIT) and VAMP2 immunolabeling. A representative confocal micrograph shows a clear lack of Alexa Fluor 488-BoNT/A-Hc uptake in the absence of high K+. Uptake of Alexa Fluor 488-BoNT/A-Hc is increased significantly in the presence of high K+ and shows a partial co-localization with VAMP2 (arrow). The arrowhead indicates an Alexa Fluor 488-BoNT/A-Hc-positive compartment that does not co-localize with VAMP2. Scale bars, 10 μm. C, level of Alexa Fluor 488-BoNT/A-Hc uptake in neuritic processes determined as described under “Experimental Procedures.” A t test revealed a significant increase (**, p < 0.01) in fluorescence intensity upon stimulation with high K+ (n = 30–38 regions of interest), two independent experiments). D, intensity of VAMP2 immunostaining determined as an internal control to ensure there was no change between tested samples (n = 30–38, two independent experiments).