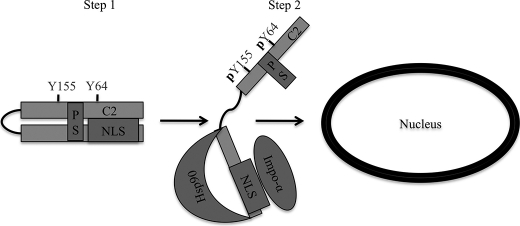
FIGURE 6.
A model for nuclear localization of PKCδ. Step 1, PKCδ is retained in the cytoplasm of resting cells through a closed conformation that is refractory to importin-α binding to the NLS in the absence of apoptotic stimuli. Step 2, in response to apoptotic stimuli, such as etoposide or H2O2, PKCδ is phosphorylated at Tyr-64 and Tyr-155. Tyrosine phosphorylation results in an open conformation of PKCδ allowing exposure of the NLS as well as binding sites for Hsp90, where importin-α and Hsp90 can bind, respectively. Once bound to importin-α, PKCδ then translocates into the nucleus. C2, C2-domain; PS, pseudosubstrate domain.