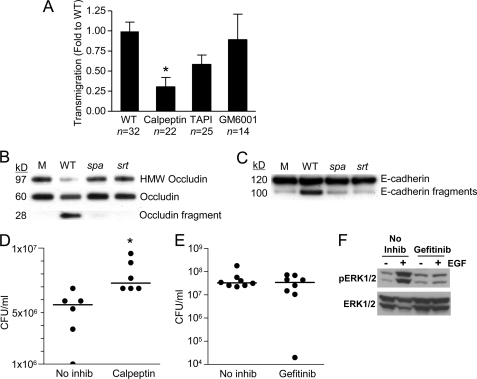
FIGURE 6.
S. aureus activates epithelial proteases. A, transmigration of S. aureus across monolayers treated with calpain inhibitor calpeptin, ADAM17 inhibitor TAPI, or a general protease inhibitor GM6001, 24 h after inoculation.*, p < 0.05 Student's t test. n for each group is shown on the figure, representative of at least two individual experiments. Error bars, S.D. B and C, generation of high molecular weight (HMW) occludin (B) and E-cadherin cleavage (C) products in Triton X-100-soluble lysates of polarized airway epithelial cells exposed to S. aureus Newman wild type (WT), spa or sortase (srt) mutants identified by immunoprecipitation and immunoblotting. D and E, CFU/ml recovered from bronchoalveolar lavage fluid of C57BL/6 mice pretreated with calpeptin (D) (*, p = 0.0043) or gefitinib (EGFR inhibitor) (E) 4 h after infection intranasally with 108 cfu S. aureus. Each dot represents one mouse, and lines represent the median for each group. F, gefitinib inhibits EGFR-dependent ERK1/2 phosphorylation in vivo. Mice were pretreated with gefitinib or vehicle (No inhib), then received an intraperitoneal injection of 1 μg of EGF or PBS, and 15 min later lungs were collected and prepared for immunoblotting. Phospho- and total ERK1/2 were detected by immunoblotting. Each lane represents one mouse; one independent experiment.