Figure 1.
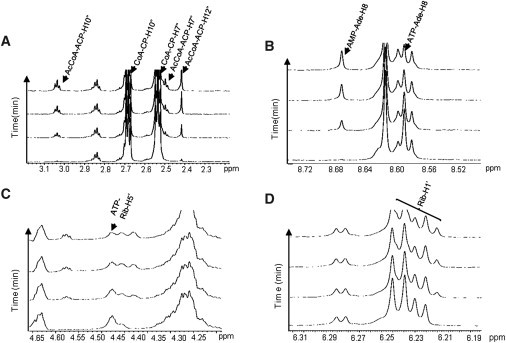
Real-time monitoring of ACS forward reaction by 1H NMR. The NMR-based assays, consisting of ATP (1.2 mM), acetate (1.0 mM), CoA (2.0 mM), and ACS (12.5 μg), were carried out at 37°C in a 600 mHz spectrometer. The first spectrum was obtained ∼2 min after the addition of enzyme, and subsequently 299 spectra were collected over a 70 min period. Representative spectra in the time course are shown. Labeled abbreviations: Ade (adenosine), Rib (ribose), ACP (acetate-cysteamine-pantothenate). (A) A portion of the 1H-observed, time-resolved spectra showing ACS conversion of CoA to AcCoA (diagnostic peaks of the protons belonging to the carbons of ACP regions at 2.2–3.2 ppm). (B) A portion of the spectra showing ACS conversion of ATP to AMP as AcCoA is synthesized (diagnostic peaks of the protons belonging to the carbons of the adenosine base of AMP or ATP at 8.4–8.7 ppm). (C) A portion of the spectra showing ACS conversion of ATP to AMP as AcCoA is synthesized (diagnostic peaks of the protons belonging to the carbons of the ribose region of ATP at 4.2–4.6 ppm). (D) A portion of the spectra showing the ribose regions (6.19–6.32 ppm) where peaks were not resolvable due to overlapping signals from different molecular species.
