Figure 2.
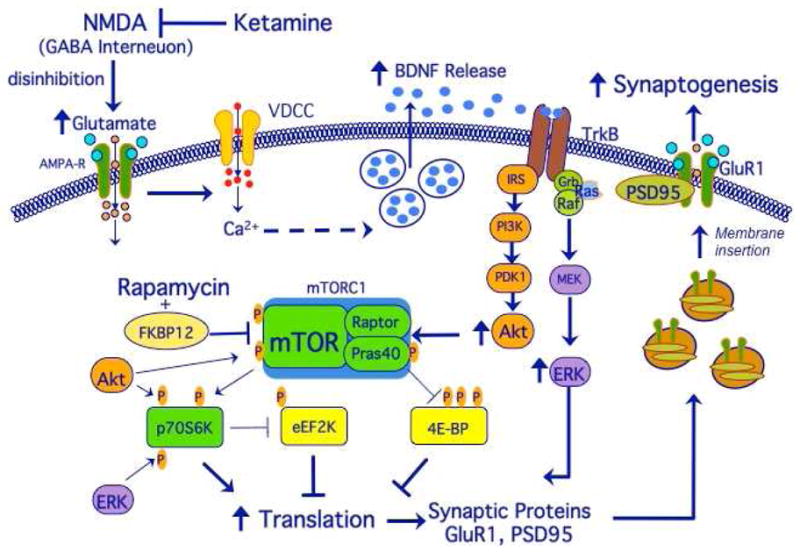
Ketamine stimulates mTOR and synaptogenesis: neurotransmitter and intracellular signaling mechanisms. Ketamine stimulates glutamate transmission, resulting in BDNF release and activation of Akt and ERK signaling, which in turn stimulate mTOR and synaptic protein synthesis. This leads to insertion of GluR1 and increased synaptogenesis, which contributes to the rapid antidepressant effects of ketamine. See text for details.
