Fig. 2.
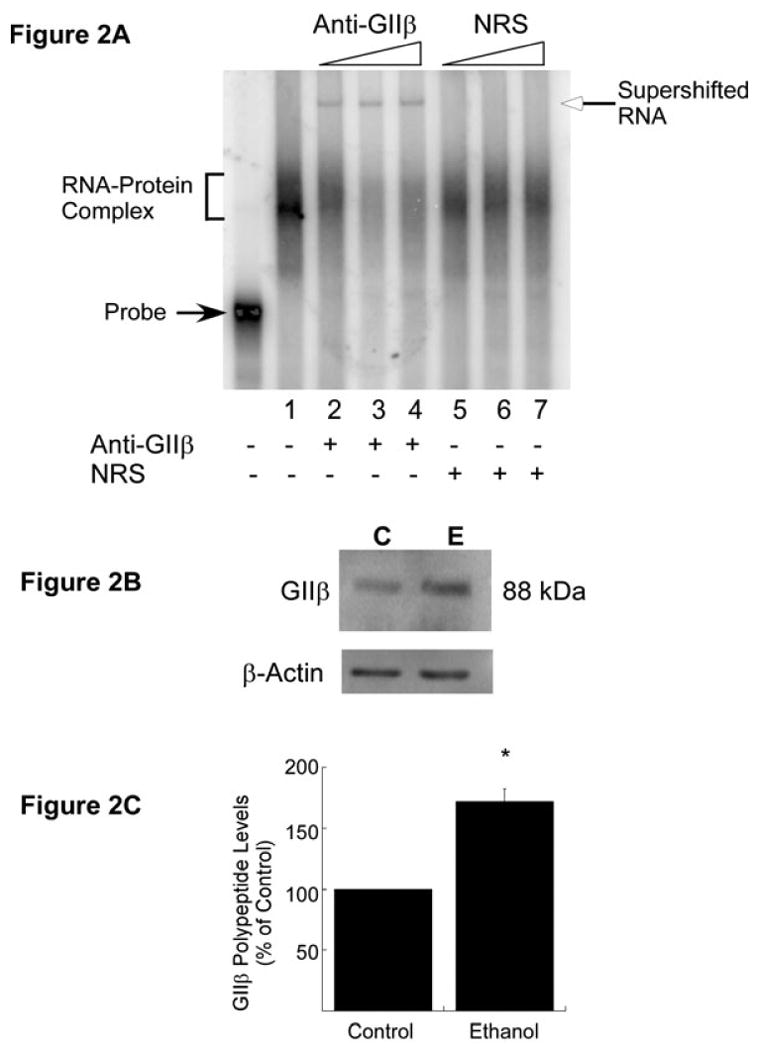
Trans-acting protein GIIβ in the CC of adult mouse. (A) RNA gel mobility supershift analysis to detect the presence of GIIβ in Δ4 RNA–CC polysomal protein complex. The [32P]-labeled Δ4 sense RNA was first incubated with CC polysomes from ethanol-exposed mice as in RNA gel shift assays. After the addition of increasing concentrations of either anti-GIIβ (lane 1, 0.04 μL; lane 2, 0.0625 μL; lane 3, 0.125 μL; lane 4, 0.25 μL of antiserum) or normal rabbit serum (NRS) (lane 5, 0.0625 μL; lane 6, 0.125 μL; lane 7, 0.25 μL), samples were further incubated at room temperature and processed as in RNA gel shift assays. A representative RNA supershift autoradiogram is shown in A. The Δ4 RNA–protein complex (bracket) and free probe (solid arrow) are indicated on the left. The addition (+) of anti-GIIβ or NRS is indicated below the autoradiogram. An increase in anti-GIIβ or NRS concentration in the reaction mix is indicated by triangles above the autoradiogram. Experiments were repeated three times with similar results. (B) In-vivo effects of chronic ethanol exposure on GIIβ polypeptide levels. CC polysomes from control (C) and ethanol-exposed (E) adult mice were separated by SDS–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, blotted onto PVDF membrane and probed with anti-GIIβ. Immunoreactive GIIβ bands were visualized using ECL Plus solution as described in Materials and methods. To control for equal loading, membranes were stripped and reprobed with anti-β-actin. (C) Quantitation of GIIβ polypeptide levels was performed using ImageQuantTL software. The signal intensity of the GIIβ-immunoreactive band was divided by the signal intensity of the β-actin band from the same lane and normalized data are expressed as a percentage of control (mean + SEM of three independent experiments). Statistical analysis was performed by ANOVA and Scheffe's test (*p<0.05).
