Figure 1.
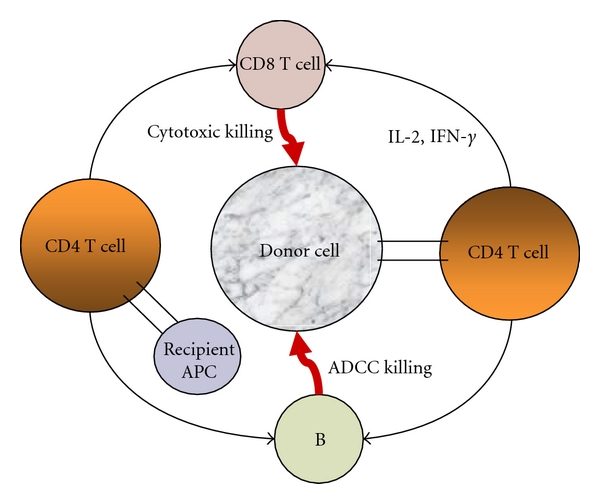
Mechanism of graft rejection. Allogeneic T cells recognize antigen through either a direct or an indirect pathway. In the direct pathway, T cells recognize intact allogeneic antigen on the surface of donor-derived APCs. This pathway is thought to predominate in acute rejection. In the indirect pathway, recipient APCs process donor-derived alloantigen into peptides and then present them to recipient T cells. This pathway is thought to dominate chronic rejection. The activation of T cells through either pathway results in killing the donor graft.
