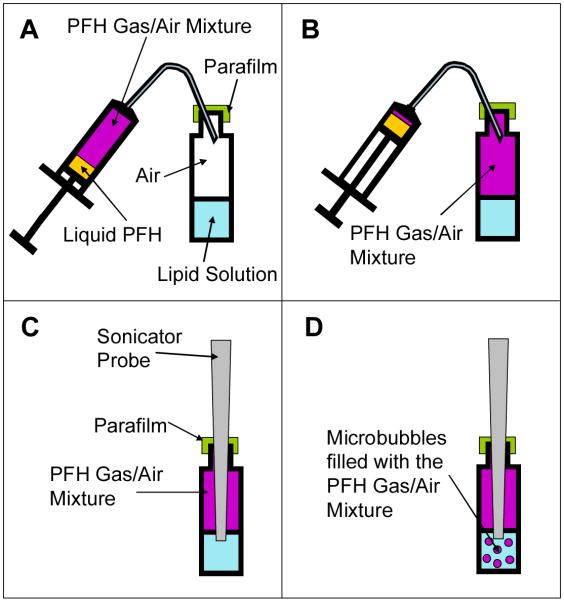
Figure 2. Schematic representation of the manufacturing process for the PFH/air mixture filled microbubbles.
(a) A 5 ml syringe is filled with 0.5 ml of liquid PFH. The PFH is allowed to evaporate and mix with the air in the syringe until it reaches equilibrium. The top of the glass vial containing the lipid solution is covered with parafilm to reduce gas exchange from within the vial to the atmosphere (b) The PFH/air mixture is injected into the head space of the vial containing the lipid solution. Care is taken to prevent injection of any liquid PFH. The original air that was in the vial is displaced through the needle track hole made in the parafilm (c) The probe sonicator tip is inserted through the parafilm into the vial and the tip is positioned 1 mm below the surface of the lipid solution. (d) The probe sonicator is turned on and creates microbubbles which incorporate the PFH/air gas mixture in the headspace. These microbubbles are coated with the lipids from the solution.