Fig. 1.
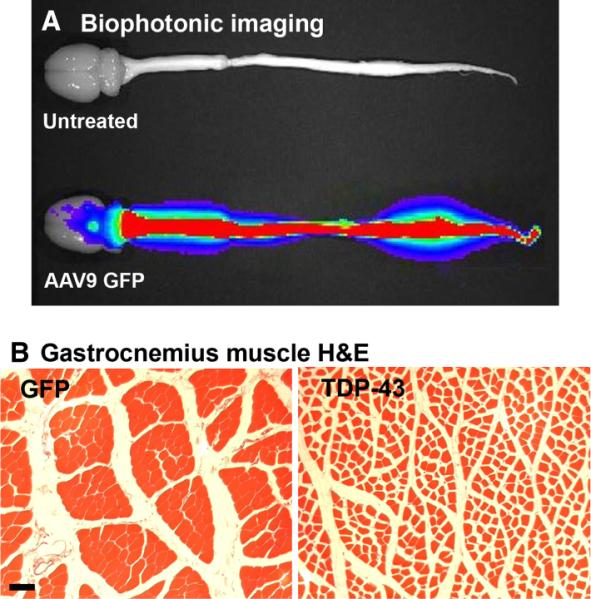
Peripheral intravenous injections of an AAV9 vector to neonatal rats led to widespread CNS expression of green fluorescent protein (GFP) or TDP-43. (A) GFP expression viewed by biophotonic imaging at 12 weeks of age. There is robust expression in the spinal cord of the GFP rat, but not in an age-matched uninjected control. The level sets of photonic emission are reflected by the color scheme, i.e. red denotes greater levels of GFP epifluorescence, and blue denotes lower levels. (B) Hematoxylin and eosin stain from the gastrocnemius muscle of a GFP rat at 4 weeks (left panel). AAV9 TDP-43 caused uniform shrinkage of myofibers indicative of widespread denervation (right panel). Bar: 67 μm for both panels in B. Reprinted from Wang et al. (2010).
