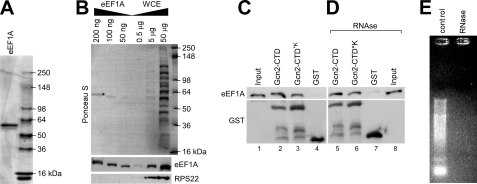
FIGURE 6.
Gcn2-CTD co-precipitates eEF1A in vitro. A, His6-eEF1A was purified from the gcn2Δ strain ESY10101 as outlined under “Experimental Procedures.” An aliquot of purified His6-eEF1A was subjected to SDS-PAGE and Coomassie staining to verify the purity of the protein. B, various amounts of purified His6-eEF1A from A, as indicated, were resolved via SDS-PAGE next to various total protein amounts of yeast whole cell extract and subjected to immunoblotting using antibodies against eEF1A and RPS22. The top panel shows Ponceau S staining of the immunoblotting membrane, and the eEF1A band is indicated with *. C, E. coli extracts harboring overexpressed GST-Gcn2-CTD, GST-Gcn2-CTD*K, or GST alone, respectively, were incubated with glutathione-linked Sepharose beads for 20 min, and then 2 μg of purified His6-eEF1A was added. After 1 h of incubation, unbound proteins were removed, and the glutathione-bound precipitates were subjected to SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting using antibodies against eEF1A and GST. The input reflects 1% of the amount of eEF1A used for each pulldown sample. D, Gcn2-CTD-eEF1A interaction in C is not mediated by RNA. The same experiment was conducted as in C, just that before starting the binding assay the E. coli extracts and eEF1A were treated with RNase A for 15 min at 4 °C. The input reflects 1% of the amount of eEF1A treated with RNase A and then used for each pulldown sample. E, RNase was functional in D. 1 μg of total yeast RNA was incubated with RNase, or not (control), using the same experimental conditions as in D, and then subjected to agarose gel electrophoresis and ethidium bromide staining.