FIGURE 2.
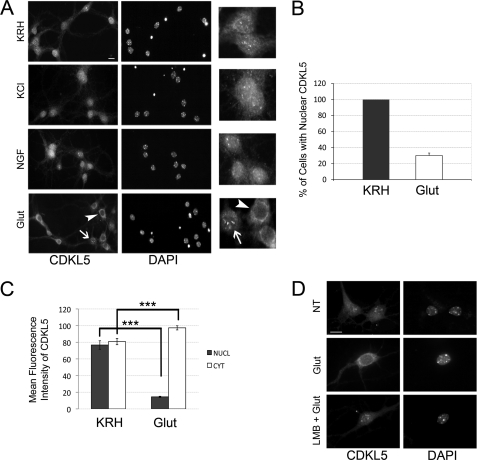
CDKL5 is actively translocated to the cytoplasm upon glutamate treatment of hippocampal neurons. A, representative immunofluorescence assays, using antibodies against CDKL5 (left panels) or DAPI staining (right panels), of unstimulated hippocampal neurons at DIV 11 (KRH) and neurons exposed for 10 min to 55 mm KCl (KCl), 100 ng/ml NGF (NGF), and 10 μm glutamate (Glut). Insets to the right show CDKL5 in treated or untreated neurons at higher magnification. B, quantification of the percentage of neurons with nuclear CDKL5 in control (KRH) or stimulated (10 μm glutamate, 10 min; Glut) conditions; data are expressed as mean of five independent experiments ± S.E. (n = 1268 neurons analyzed). C, quantification of nuclear and cytoplasmic distribution of CDKL5 in control (KRH) or stimulated (Glut) neurons (means ± S.E.; ***, p < 0.001; a total of 200 neurons were examined). D, at DIV 11, embryonic hippocampal neurons were left in KRH or stimulated with 10 μm glutamate as above (Glut). In the lower panels (LMB + Glut), neurons were treated with 100 nm LMB for 3 h before adding glutamate. Representative images of cells stained with anti-CDKL5 antibody and DAPI are shown. The scale bars are 10 μm.