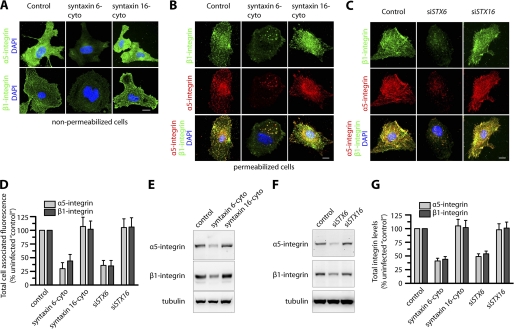
FIGURE 3.
Inhibition of syntaxin 6 function decreases α5β1 integrin levels, both cell surface-localized and total in endothelial cells. Uninfected (Control), syntaxin 6-cyto-, syntaxin 16-cyto-, siSTX6-, or siSTX16-expressing HUVECs were cultured on fibronectin-coated surfaces in complete medium. A, cells were pre-treated with Abs against α5 and β1 integrin at 4 °C prior to fixation and labeling with Alexa 488-labeled secondary Ab. Samples were then imaged by epifluorescence microscopy; representative images show cell surface levels of α5 and β1 integrins. B and C, cells were fixed and permeabilized, labeled with Abs against α5 or β1 integrin, and then labeled with the appropriate fluorescently tagged secondary Ab. Representative images obtained by epifluorescence microscopy show localization of total cell-associated α5 and β1 integrins. D, quantification of total cellular α5 and β1 integrin in syntaxin 6-cyto-, syntaxin 16-cyto-, siSTX6-, or siSTX16-expressing cells. Epifluorescence images were acquired and total cell-associated fluorescence was quantified by image analysis. Values represent relative change in the levels of α5 or β1 integrin normalized to an arbitrary value of 100% for untreated controls. Results are expressed as mean ± S.D. (n = 70 cells for each condition, from 3 separate experiments; p ≤ 0.001). E and F, Western blotting to assess α5 and β1 integrin levels in cell lysates. A representative blot is shown. G, α5 and β1 integrin band densities from E and F were quantified; values represent relative levels of α5 and β1 after normalization to the arbitrary value of 100 for uninfected cells (Control). (mean ± S.D.; n = 3; p ≤ 0.005). Scale bars represent 5 μm.