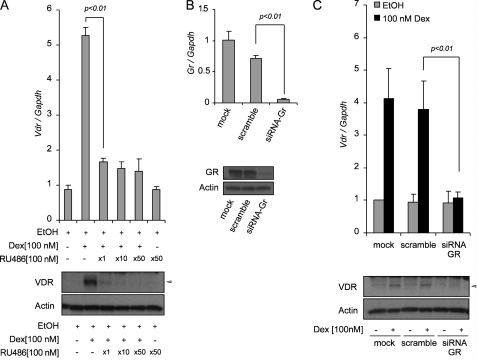
FIGURE 4.
Dexamethasone increases de novo Vdr transcription in a GR-dependent manner. A, the anti-glucocorticoid RU486 inhibits Vdr mRNA synthesis. The cells were treated for 24 h with 100 nm Dex alone or in combination with 1, 10, or 50 molar ratios of RU486. Expression of VDR was assessed at the transcriptional level (upper panel) and protein (lower panel) by using real time PCR and Western blot analysis, respectively. B, silencing of GR by using siRNA. The cells were transfected with mock, scramble siRNAs, or siRNA-GR. After 72 h, the cells were harvested, and expression of GR was assessed at the transcriptional level (upper panel) and protein (lower panel) by using real time PCR and Western blot analysis, respectively. C, induction of Vdr by Dex was studied in cells transfected with siRNA targeting Gr. The cells were transfected with mock, scramble siRNAs, or siRNA-GR for 48 h prior to treatment with 100 nm Dex or EtOH vehicle control for an additional 24 h. Expression of VDR was assessed at the transcriptional level (upper panel) and protein (lower panel) by using real time PCR and Western blot analysis, respectively. The expression of Vdr (A and C) and Gr (B) was assessed by real time PCR using TaqMan® gene expression assays. Relative expression of Vdr (A and C) and Gr (B) gene was normalized to mouse glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (Gapdh) expression and expressed relative to EtOH vehicle control (A) or compared with the ethanol-treated mock control (B and C). The data represent the means ± S.D. of three independent experiments.