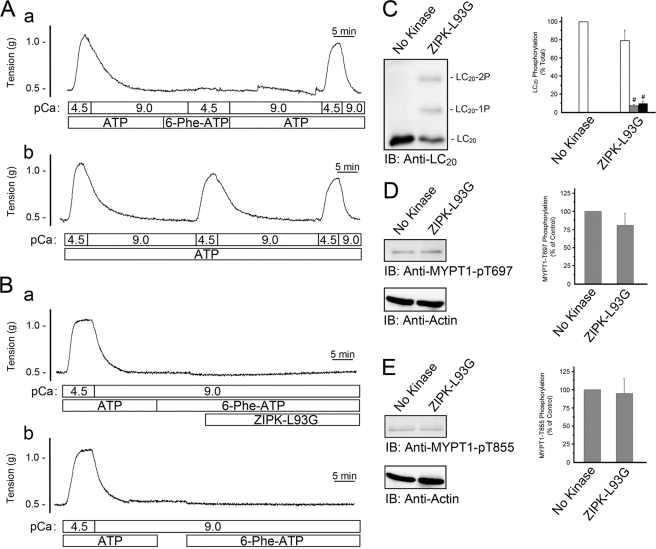
FIGURE 8.
Effect of ZIPK-L93G in the presence of N6-phenyl-ATP on LC20 and MYPT1 phosphorylation in Triton-skinned rat caudal arterial smooth muscle. A, trace a, following an initial control Ca2+-induced contraction-relaxation cycle, ATP was washed out of the system. The effective removal of ATP was verified by the lack of a contractile response to the addition of N6-phenyl-ATP at pCa 4.5. Subsequent replenishment with ATP restored Ca2+-induced contraction. Trace b, repeated Ca2+-induced contractions were recorded when ATP was maintained throughout the experiment. B, following initial control Ca2+-induced contraction-relaxation cycles, ATP was washed out of the system. N6-phenyl-ATP (4 mm) was then added in the presence (trace a) or absence (trace b) of ZIPK-L93G (10 μm) at pCa 9. Tissues were then quick-frozen for analysis of LC20 phosphorylation by Phos-tag SDS-PAGE and Western blotting with anti-LC20 (IB), and band intensities were quantified by scanning densitometry (C). Values indicate mean ± S.E. (n = 6). MYPT1 phosphorylation was analyzed by Western blotting with phosphospecific antibodies, anti-phospho-Thr-697-MYPT1 (D), and anti-phospho-Thr-855-MYPT1 (E). MYPT1 phosphorylation levels were normalized to actin, and the results are expressed relative to the control (No Kinase). #, significantly different from control (Student's t test, p < 0.05).