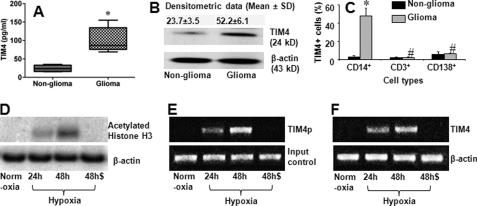
FIGURE 1.
TIM4 is detected in glioma tissue. Total proteins were extracted from each surgically removed glioma tissue and normal tissue (marginal non-glioma; proved by a pathologist) to assess the TIM4 levels by ELISA (A) and Western blotting (B). A, levels of TIM4 determined by ELISA. B, TIM4 blots. C, single cells were prepared with the surgically removed glioma tissue and non-glioma tissue. The cells were stained with antibodies against TIM4, CD14, CD3, and CD138 and analyzed by flow cytometry. Bars indicate the frequency of TIM4+ cells in CD14+, CD3+, or CD138+ cells. Each specimen was processed individually. The data are presented as means ± S.D. from 25 patients. *, p < 0.01 compared with the non-glioma tissue; #, p < 0.01 compared with the group of CD14+ cells. D–F, data from ChIP assay. D, blots of acetylated histone H3 (upper panel). E, expression of the TIM4 promoter (TIM4p; upper panel). F, expression of TIM4 mRNA (upper panel). The data in D–F represent three experiments. Cells were cultured under normoxia or hypoxia. Cells cultured under hypoxia were cultured for 24 or 48 h as indicated with (48h$) or without (48h) the anti-HIFα1 antibody (500 ng/ml) added to the culture medium. Samples from patients were analyzed individually.