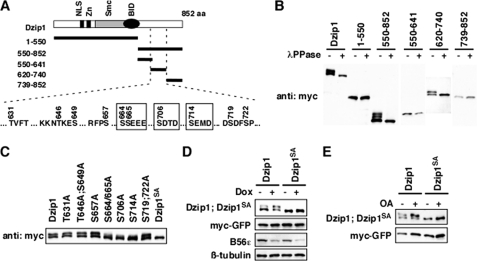
FIGURE 4.
B56-containing PP2As dephosphorylated Dzip1 at Ser-664/665/706/714. A, shown is a schematic representation of Dzip1 deletion constructs used to identify phosphorylation sites of Dzip1. All potential phosphorylation sites within residue 620–740 are listed. The four CK2 sites are highlighted in boxes. aa, amino acids. NLS, nuclear localization signal. B, shown is phosphorylation of Dzip1 deletions. Dzip1 deletion constructs were transfected into HEK293T cells and subjected to Western blot analysis. All deletions carrying 620–740 are phosphorylated, as judged by mobility shift of proteins on SDS-PAGE. λPPase, λ-protein phosphatase. C, shown is phosphorylation of Dzip1 mutants. Dzip1 mutants were transfected into HEK293T cells and analyzed by Western blotting. Whether a protein is phosphorylated is judged by the mobility shift of protein on SDS-PAGE. Mutations of Ser-664, -665, -706, or -714, but not other potential kinase recognition sites, impaired phosphorylation of Dzip1. Dzip1 with Ser-664/665/706/714 mutated is denoted as Dzip1SA. D, knockdown of B56s had no effect on the phosphorylation status of Dzip1SA. Dzip1 and Dzip1SA were transfected into PC6-3 cells. Cells were treated with Dox to induce B56s knockdown. Phosphorylation of Dzip1 and Dzip1SA was assayed. Note that knockdown of B56s failed to alter the migration rate of Dzip1SA on SDS-PAGE. E, inhibition of PP2A had no effect on the phosphorylation status of Dzip1SA. Dzip1 and Dzip1SA were transfected into NIH3T3 cells. Cells were treated with OA to inhibit PP2A. Western blot was performed to assay the phosphorylation status of Dzip1 and Dzip1SA.