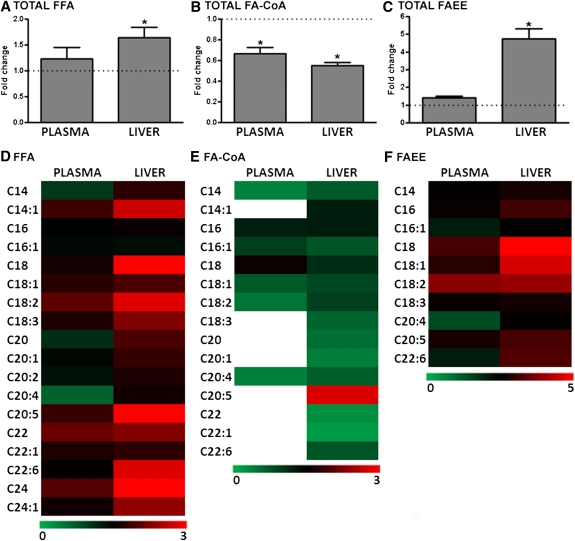
Fig. 1.
Relative levels of plasma and liver fatty acid metabolites in alcohol-fed mice. (A) The changes in plasma and hepatic total FFAs are shown for alcohol-fed mice (n = 11) relative to control mice (n = 8). In control mice, plasma total FFA levels are unchanged, whereas there is a significant increase in hepatic FFA levels for alcohol-fed mice. (B) Plasma and liver total FA-CoA levels are decreased in alcohol-fed mice. (C) Alcohol feeding is associated with a higher level of total FAEE in the liver; however there was no significant change in the plasma. Data are means ± SEM. Heat maps showing the relative change in plasma (left column) and hepatic lipids (right column) of different carbon-chain lengths are provided for FFA (D), FA-CoA (E), and FAEE (F). *P < 0.05 alcohol-fed versus control mice.