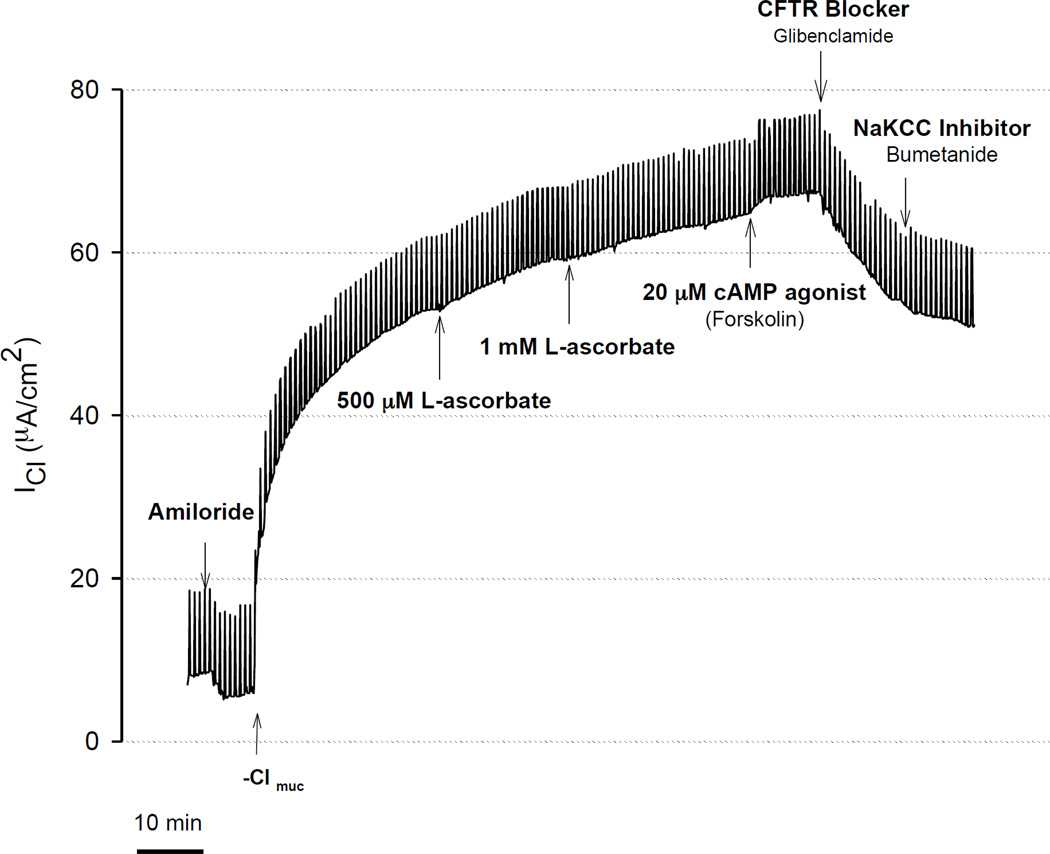
Figure 4.
Stimulation of transepithelial Cl secretion by L-ascorbate and cAMP agonist (forskolin) in freshly excised sinus tissue from CRS patient. Transepithelial Cl currents (ICl) were measured in the presence of the sodium channel blocker amiloride (10 µM) and a serosal-to-mucosal directed Cl gradient (−Clmuc). Gradient driven Cl currents (ICl) stabilized after ~30 minutes. Addition of increasing concentrations of L-ascorbate (500 µM, 1 mM) to the mucosal surface stimulated ICl in a dose-dependent fashion. L-ascorbate stimulated ICl was further activated by the cAMP agonist forskolin (20 µM) and sequentially blocked by the CFTR blocker glibenclamide (1 mM) and NaKCC inhibitor bumetanide (200 µM). In this experiment, Cl secretion was stimulated by ascorbate to 80.6% of the currents elicited by forskolin.