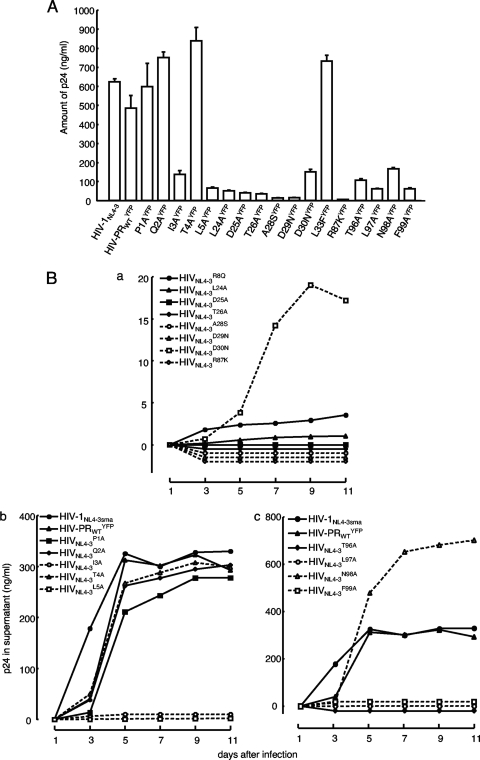
Fig. 4.
Replication kinetics of HIV-PRYFP with wild-type or mutated PR. (A) 293T cells were transfected with pHIV-PRWTYFP or mutated pHIV-PRYFP (if pHIV-PRP1AYFP was used, it is shown as P1AYFP), and the amounts of p24 Gag in the culture supernatants were determined 48 h after transfection. (B) MT-4 cells (105) were exposed to the harvested supernatant of each infectious HIV-PRYFP clone shown in panel A (100 ng of p24 Gag protein/ml) for 6 h, washed twice with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS), and further cultured in 7 ml of complete medium. Culture supernatants (50 μl) were harvested every other day, and virus replication was monitored by the amounts of p24 Gag produced in the culture supernatants. Replication kinetics of various HIV-PRYFP mutants are shown over 11 days. In subpanels a, b, and c, the replication kinetics of infectious clones carrying mutations in the active site, N ternimus, and C terminus, respectively, are shown. Note that recombinant HIV clones, whose replication rates were relatively poor, are illustrated in subpanel a. The experiments that generated data in subpanels a and b were performed on the same occasion. Thus, two controls (HIV-1NL4-3sma and HIV-PRWTYFP) in subpanel b serve as controls in subpanel a as well.