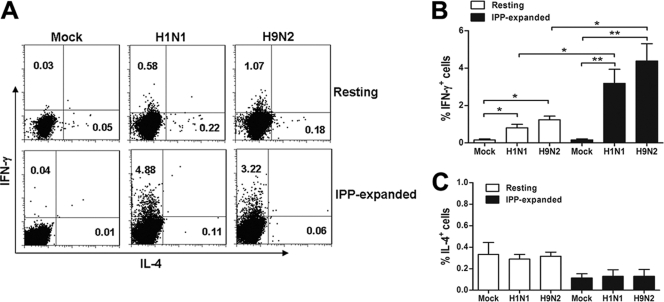
Fig. 1.
Human Vγ9Vδ2 T cells express type 1 cytokines in response to FluA viruses. (A) PBMCs were infected by FluA H1N1 or H9N2 virus at an MOI of 2 for 12 h (upper row). MDMs were infected by H1N1 or H9N2 virus (target) at an MOI of 2 for 1 h and then cocultured with the purified IPP-expanded Vγ9Vδ2 T cells (effector) at an effector-to-target ratio of 1:1 for 12 h (lower row). Cells were stained for CD3, TCR γδ, IFN-γ, and IL-4. The intracellular contents of IFN-γ (y axis) and IL-4 (x axis) in resting γδ T cells and IPP-expanded γδ T cells are representative of six separate experiments. (B) The percentages of IFN-γ+ cells in resting and IPP-expanded γδ T cell populations (means ± SEM) are shown (n = 6). (C) The percentages of IL-4+ cells (means ± SEM) in resting and IPP-expanded γδ T cell populations are shown (n = 6). *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01.