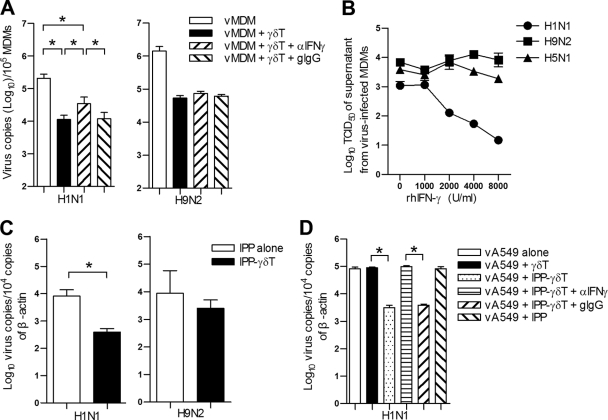
Fig. 5.
IFN-γ released from Vγ9Vδ2 T cells inhibits human seasonal H1N1 virus replication but not avian FluA viruses. (A) MDMs were infected with H1N1 or H9N2 virus at an MOI of 2 for 1 h. Then vMDMs were cultured alone or with purified IPP-expanded Vγ9Vδ2 T cells at an effector/target ratio of 10:1 in the presence of anti-IFN-γ MAb (αIFN-γ; 10 μg/ml) or its isotype control, goat IgG (gIgG; 10 μg/ml), for 48 h. Total RNA was extracted from both cells and supernatants, and viral M1 gene copies were quantified by real-time RT-PCR. Data (means ± SEM) for M1 gene copies per 105 MDMs from four separate experiments are shown. (B) MDMs were pretreated with human recombinant IFN-γ at the indicated doses for 24 h and then infected with H1N1, H9N2, or H5N1 virus at an MOI of 2 for an additional 48 h. The virus titers of supernatants were determined by TCID50 assay on MDCK cells. Data are means ± SEM of TCID50 titers of four separate experiments. (C) A549 cells (target) were infected by human seasonal H1N1 or avian H9N2 virus at an MOI of 2 for 1 h. Purified Vγ9Vδ2 T cells (effector) were added into transwell inserts at an effector-to-target ratio of 5:1 in the presence of IPP (6 μg/ml) and cocultured for 4 days. In the control group (IPP alone), IPP was added to infected A549 cells in the absence of Vγ9Vδ2 T cells. (D) A549 cells in the bottom wells were infected by H1N1 virus at an MOI of 2. Purified Vγ9Vδ2 T cells were added into transwell inserts. IPP (6 μg/ml) was added alone or together with anti-IFN-γ MAb (10 μg/ml) or goat IgG (10 μg/ml); The A549 cells were collected at day 4 postinfection. Viral copies were quantified by real-time PCR. Data are means ± SEM for viral M1 gene copies per 104 copies of β-actin from four separate experiments. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01.