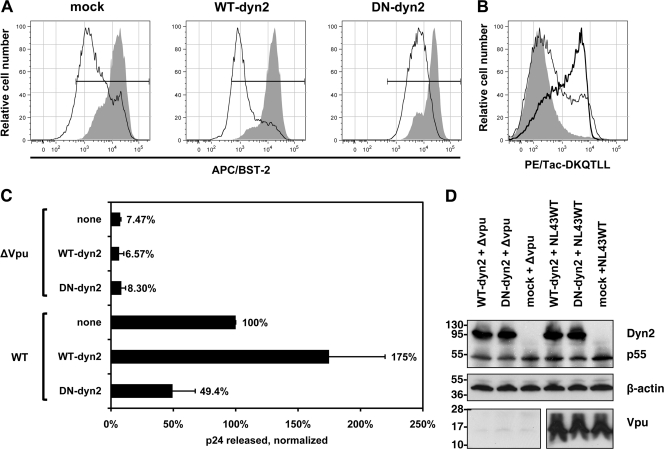
Fig. 1.
Dominant negative dynamin 2 inhibits the Vpu-mediated downregulation of BST-2 and the enhancement of virion release. (A) Inhibition of Vpu-mediated downregulation of cell surface BST-2 by dyn2K44A. Cells (HeLa, which express BST-2 constitutively) were transfected to express dynamin 2 (WT-dyn2; 1.2 μg of plasmid), the dominant negative mutant dyn2K44A (DN-dyn2; 1.2 μg of plasmid), or an irrelevant protein (HLA-A2 [“mock”]; 1.2 μg of plasmid), together with GFP as a transfection marker (0.2 μg of plasmid) and either with or without Vpu (0.2 μg of plasmid expressing Vpu or pCIneo as an empty vector control). The next day, the cells were stained and analyzed by flow cytometry for GFP expression and surface BST-2. Histograms show the relative number of cells versus BST-2 (APC) fluorescence intensity for the GFP-positive cells. Shaded histograms represent cells not expressing Vpu; open histograms represent cells expressing Vpu. Horizontal bars indicate the BST-2-positive gate set using an isotype-matched control antibody. (B) Upregulation of the endocytic indicator protein Tac-DKQTLL by dyn2K44A. Cells (HeLa) were transfected to express Tac-DKQTLL (0.2 μg of plasmid) and GFP (0.2 μg of plasmid) along with either dynamin 2 (thin line) or the dominant negative mutant dyn2K44A (thick line), as described above, or transfected to express GFP and Tac-DKQTLL only (shaded) and then stained the next day for surface Tac antigen and analyzed by flow cytometry. Histograms show the relative number of cells versus Tac (PE) fluorescence intensity for the GFP-positive cells. (C) Inhibition of Vpu-mediated enhancement of virion release by dyn2K44A. Cells (HeLa) were transfected to express the indicated complete viral genomes (0.4 μg of plasmid) along with either dynamin 2 (WT-dyn2; 1.2 μg of plasmid), dyn2K44A (DN-dyn2; 1.2 μg of plasmid), or an irrelevant protein (HLA-A2 [“none”]; 1.2 μg of plasmid). The next day, culture supernates were collected, and the concentration of p24 capsid antigen was measured by ELISA. The data were normalized by setting wild-type virus in the absence of either dynamin 2 overexpression or the dominant negative dyn2 expression (“none”) to 100%. Data were obtained from duplicate transfections. (D) Verification of the expression of dynamin 2 (WT-dyn2), dyn2K44A (DN-dyn2), HIV-1 Gag precursor (p55), and Vpu during the virion release experiments by immunoblotting; the dynamin 2 proteins were detected using an antibody recognizing their polyhistidine tags.