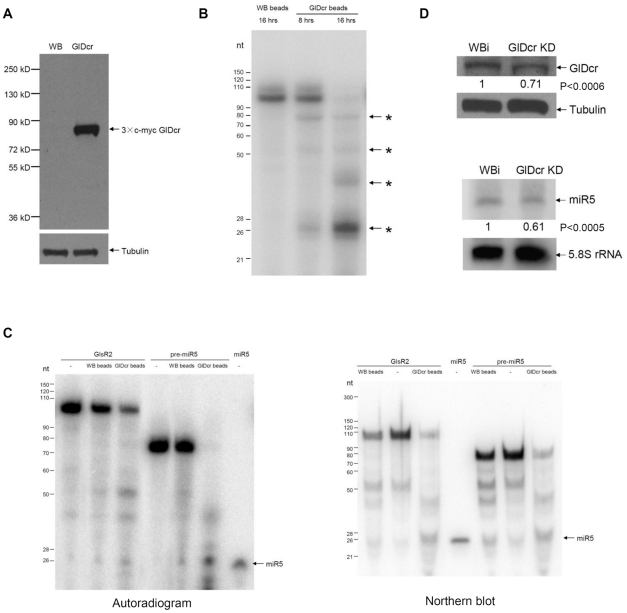
Figure 4. GlDcr is required for processing GlsR2 to generate miR5.
(A) Western blot of 3×c-myc GlDcr that was immunoprecipitated using the anti-c-myc antibody. GlDcr: 3×c-myc GlDcr over-expressing cells. WB: un-transfected cells. Tubulin: loading control. (B) In vitro dicing of a 106 bp 32P-dsRNA. The labeled dsRNA was incubated with the immunoprecipitate from the untransfected cells (WB beads, left lane) and the transfected cells (GlDcr beads, center and right lanes) and incubated at 37°C for 8 or 16 hrs. The smaller RNA fragments were shown with asterisks. (C) In vitro dicing of GlsR2 and the 75 nt pre-miR5. Left panel: The purified GlDcr beads were incubated with the radiolabeled substrates at 37°C for 16 hours and analyzed with RNA PAGE and autoradiography. In vitro transcribed GlsR2 and pre-miR5 incubated with water (-) and WB beads were included as controls. Right panel: Unlabeled GlsR2 and pre-miR5 were digested by the GlDcr beads. After RNA PAGE, the gel was blotted and analyzed by a Northern using end-labeled anti-miR5 as probe. WB beads and water (-) were also included as the controls. (D) GlDcr is essential for biogenesis of miR5. Upper panel: Western blot using anti-GlDcr polyclonal antibody showed that GlDcr was knocked down by 29% in GlDcr knockdown (GlDcr KD) cells. WBi was the control cells and Tubulin was the loading control. Lower panel: Northern blot shows that the endogenous miR5 level was decreased by 39% in GlDcr KD cells. The 5.8S rRNA was used as a loading control. The results were from three independent experiments. The p-values indicated were calculated by two-tailed Student's t-test.