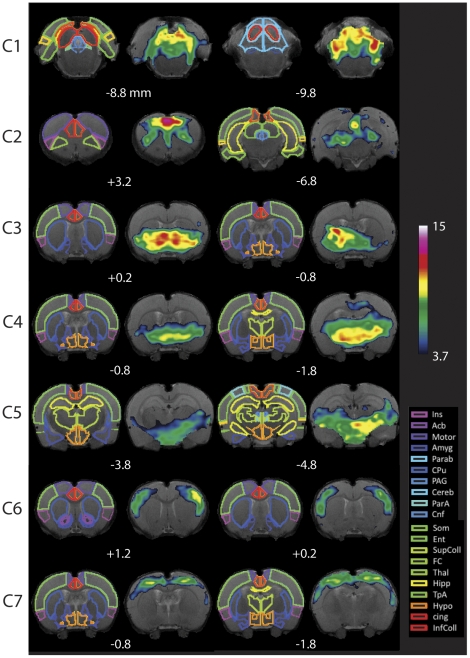
Figure 3. Resting State Networks in Awake Rats.
Components (C1–C7) are ordered according to their reproducibility degree. Component 1 has significant cerebellar structures; Component 2 includes medial and lateral cortical structures resembling the human default mode network; Component 3 includes a basal-ganglia-hypothalamus network; Component 4 encompasses basal-ganglia-thalamus-hippocampus circuitry; Component 5 represents an autonomic pathway; Component 6 represents the sensory network; and Component 7 groups interoceptive structures to form a network. All components have been thresholded according to a mixture model approach-see Methods for details. The atlas is based on the Paxinos Atlas (Paxinos and Watson [33]). Key: Ins: Insula, AcB: Nucleus Accumbens, Motor: Motor Cortex, Amyg: Amygdala, Parab: Parabrachial, CPu: Caudate-Putamen, PAG: Periaqueductal Gray, Cereb: Cerebellum, ParA: Parietal Association Cortex, Cnf: Cuneiform nucleus, Som: Somatosensory Cortex, Ent: Entorhinal Cortex, SupColl: Superior Colliculus, FC: Frontal Cortex, Thal: Thalamus, TpA: Temporal Association Cortex, Hypo: Hypothalamus, cing: Cingulate cortex (anterior and retrosplenial), InfColl: Inferior Colliculus.