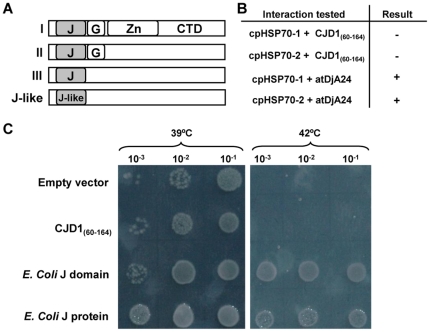
Figure 4. Assay of CJD1 J-like domain as a possible co-chaperone.
A, Modular organization and classification of the different types of J proteins (I, II, III and J-like) proposed by [25]. J, J domain; G, Glycine rich domain; Zn, Zn-finger domain; CTD, C-terminal domain. B, Results of Y2H experiments with the two Arabidopsis chloroplastic HSP70 proteins and CJD1 J-like domain or atDjA24 HSP40 co-chaperone J-domain. C, The J-like domain of CJD1 does not rescue the temperature sensitivity of an E. coli dnaJ/cbpA double knockout mutant. The empty vector and CJD160–164 transformed mutants were viable at 39°C, but inviable at 42°C, while the cells transformed with the full E. coli DnaJ protein and only the J domain were viable at both temperatures. Cells were spotted on LB media supplemented with 0.5% w/v arabinose and 20 µg/ml ampicillin.