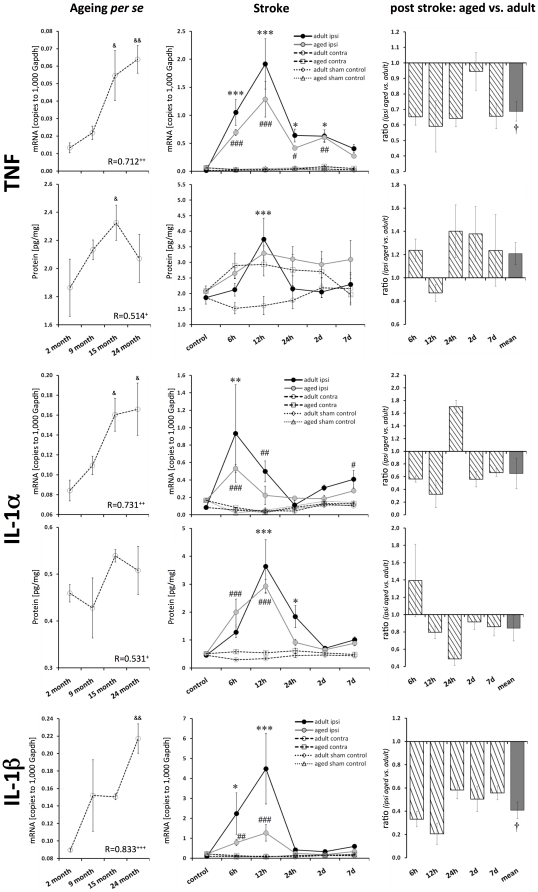
Figure 2. Age- and stroke-dependent expression of TNF, IL-1α, and IL-1β.
TNF, IL-1α, and IL-1β displayed significantly elevated expression levels with age. All these pro-inflammatory cytokines showed a distinct response following stroke, which was attenuated in aged brains. Expression values are shown as mean ± SEM and ratios as geometric mean ± SEM. Significant age-related differences (versus 2-month-old native mice) are indicated by & p≤0.05, && p≤0.01, and &&& p≤0.001 (ANOVA and post-hoc Tukey test). Correlation of the cytokine expression level with age is indicated by + p≤0.05, ++ p≤0.01, and +++ p≤0.001 (R, Pearson correlation). Significant post-stroke differences (ipsi versus contra) are indicated by adult: * p≤0.05, ** p≤0.01, and *** p≤0.001; and aged: # p≤0.05, ## p≤0.01, and ### p≤0.001 (paired two-way ANOVA and post-hoc Tukey test). Significant age-dependent differences after stroke (ipsi aged versus ipsi adult) are displayed by † p≤0.05, †† p≤0.01, and ††† p≤0.001 (two-way ANOVA).