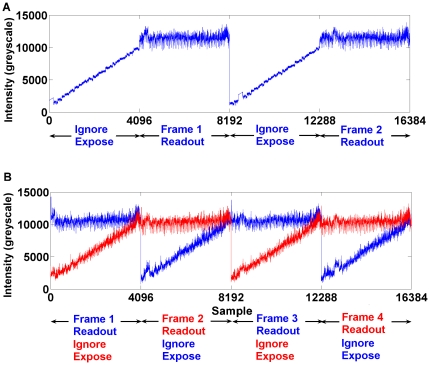
Figure 11. Example raw data traces.
A) An example trace of the raw data obtained during readout of one channel. Although the sensor is first exposed and then read out sequentially, pixels are sampled continuously at a constant (synchronised) rate. During the exposure time samples are acquired but are simply discarded (marked ‘Ignore’), while during the readout time (marked ‘Read’) the sensor is blind and does not collect photons. B) Raw data obtained during readout in dual-channel mode. Exposure and readout alternate on two channels. This means the photodiode on each pixel is able to collecting photons continuously and simply alternate which storage capacitor it uses. In this way the frame rate is doubled and the dead-time can be virtually eliminated.