Table 1. N- and C- terminal sequences of the circularly permuted GroEL subunits constructed in this study.
| Mutant | Corresponding sequence in WT | C-terminal sequence | N-terminal sequence |
| CP209 |
206
Asn-Lys-Pro-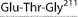
|
Asn-Lys-Pro C |
N
Met-
|
| CP254 |
251
Ala-Glu-Asp-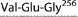
|
Ala-Glu-Asp -Val-Ala-Asn C |
N
Met-Ala-Ala-Ala-Gln-Tyr-
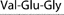
|
| CP376 |
372
Lys-Leu-Gly-Gly-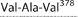
|
Lys-Leu-Gly -Ala-Asn C |
N
Met-Ala-Gly-Gly-Ala-
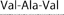
|
| CP376-RW |
372
Lys-Leu-Gly-Gly-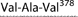
|
Lys-Leu-Gly-Ala-Asn C |
N
Met-Gly-Ala-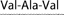
|
Underlines and <$>\scale 90%\raster="rg1"<$>wavy underlines are added to highlight corresponding sequence elements between each CP mutant and wild type (WT). Sequences in italics denote amino acids that are not from the native sequence of GroEL, added as a consequence of the circular permutation protocol. In addition, we found that in CP376, the N-terminal amino acid sequence had been altered, and apparently insertion of an extra alanine residue had occurred (double underlined). We decided to name this mutant CP376 based on the fact that the native GroEL amino acid sequence continues uninterrupted after Val376. GroEL CP376-RW contains an additional Arg to Trp point mutation at the position corresponding to Arg231 in the wild type sequence.
