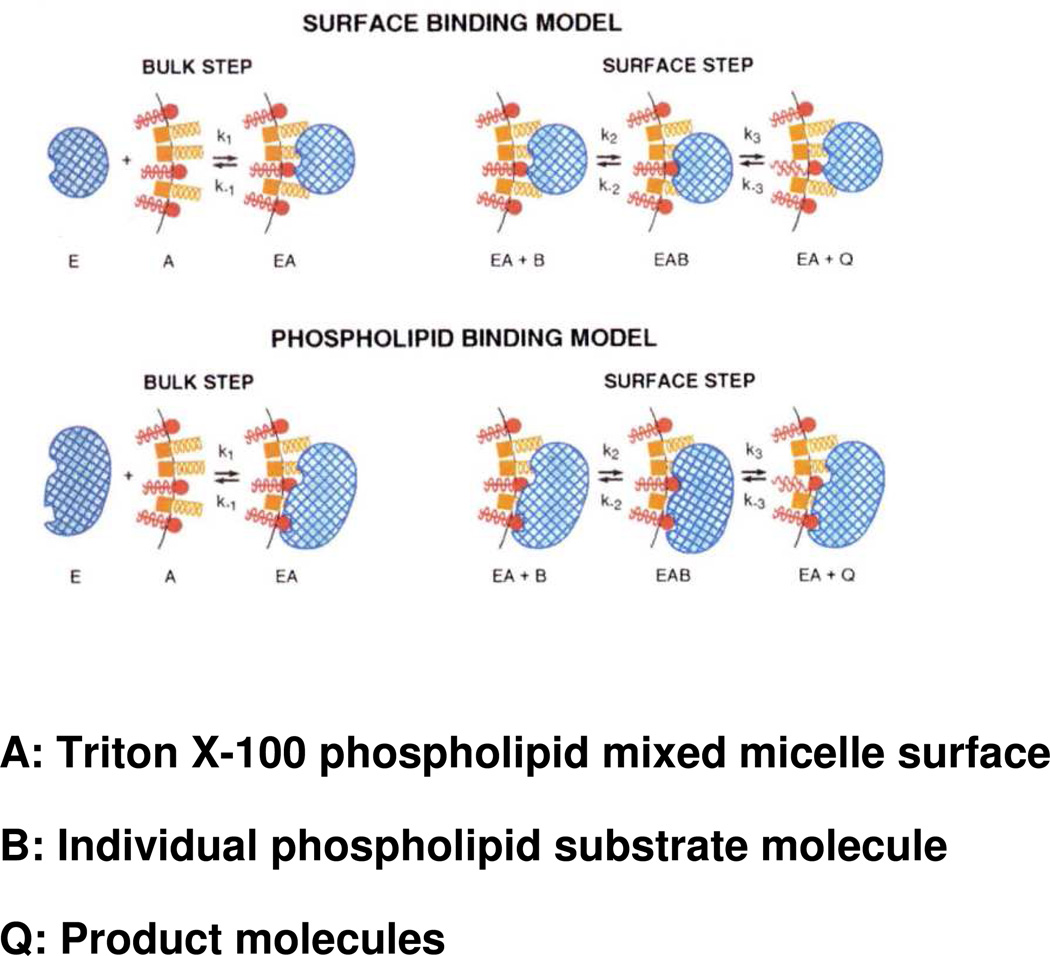
Figure 2.
Illustration of the application of “surface dilution kinetics” to the phospholipase A2-catalyzed hydrolysis of phospholipids contained in mixed micelles with nonionic surfactants such as Triton X-100. Two possibilities are shown: top, the “surface binding model” whereby the enzyme first associates nonspecifically with the micelle surface; and bottom, the “phospholipid binding model” whereby the enzyme first associates specifically with phospholipid in the micelle surface. In both cases, in a subsequent step, the enzyme associated with the micelle binds a phospholipid substrate molecule in the micelle in its catalytic site and carries out hydrolysis producing as products a lysophospholipid and a fatty acid, which may be released to solution or be retained in the micelle surface. Phospholipid molecules are depicted in red, detergent molecules in gold, and enzyme in blue. Adapted from Ref.24