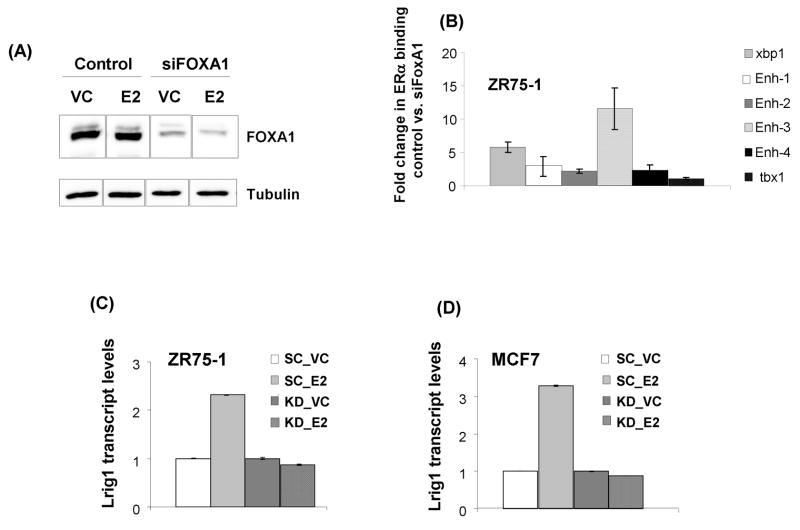
Figure 5.
E2-mediated regulation of Lrig1 is FOXA1-dependent. (A) Representative western blot of FOXA1 knockdown efficiency. Hormone starved ZR75-1 cells were treated with either scramble control or FOXA1 siRNA. The following day the medium was changed to include either vehicle control (VC) or 10 nM E2 for an additional 24 hours. Cell lysates were collected at 48 hours post-transfection. (B) Hormone starved ZR75-1 cells were treated with either scramble control or FOXA1 siRNA 48 hours prior to treatment with 10 nM E2 or VC for 30 minutes followed by cross-linking. Chromatin immunoprecipitation was performed with antibodies against ERα and subjected to qPCR with primers against the indicated regions. Xbp1 enhancer 1 served as a positive control while the Tbx1 enhancer (FOXA1-independent) served as a negative control. Results are plotted as fold change in ERα occupancy, comparing scramble control and FOXA1 siRNA treatment. Shown is the mean of three independent replicates with standard deviation. Hormone starved ZR75-1 (C) and MCF7 (D) cells were treated with either scramble control or siRNA to FOXA1. Cells were then treated with either vehicle control (VC) or E2 for 8 hours before harvesting. Lrig1 transcript abundance was measured using Taqman real-time qPCR. Experiments were performed in triplicate and repeated at least three times with a representative experiment shown.