Figure 3. Vitamin D3 synthesis and signaling within human primary breast adipocytes.
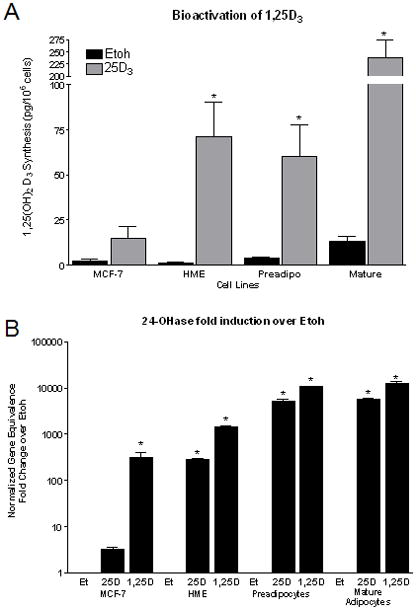
A) Breast cancer cells (MCF-7, negative control), non-transformed human mammary epithelial cells (HME, positive control), preadipocytes and mature adipocytes were treated with vehicle (Etoh) or 25D3 for 24h to assess the ability of breast adipocytes to bioactivate 25D3 to the active form, 1,25D3. Culture media was immunoextracted using a 1,25D3 Enzyme ImmunoAssay. Data are expressed as pg/ml/106 cells. B) Bioactivation and signaling through the VDR to regulate 24-OHase, a vitamin D3 target gene. 24-OHase gene induction by 25D3 and 1,25D3 in primary preadipocytes and mature adipocytes compared to HME cells (positive control) and MCF-7 breast cancer cells (negative control). 24-OHase mRNA expression was normalized to 18S from cultured cells treated for 48h with ethanol (Et), 25D3, or 1,25D3. Vehicle treated cells provided the baseline level of 24-OHase expression and 1,25D3 provided the upper level of 24-OHase expression in each cell line. *- p <0.05 compared to vehicle control in each cell line.
