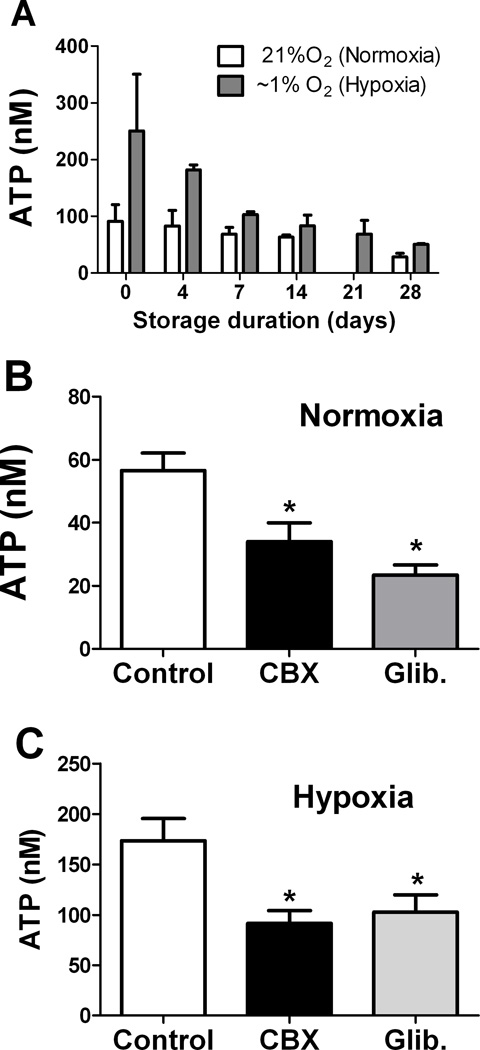
Figure 1. Basal and stimulated release of ATP from RBCs declines during conventional storage.
(A) RBCs sampled at varying times after collection and storage were added to chambers filled with Krebs buffer and bubbled with normoxic (21% O2) or hypoxic (~1% O2) gas. Extracellular ATP was measured by the luciferase assay in the supernatant of centrifuged samples. Normoxic ATP release was not assayed at 21 days. (B, C) Influence of glibenclamide (Glib.) or carbenoxolone (CBX) on ATP release from fresh RBCs in (B) normoxia or (C) hypoxia. * = p<0.05 compared to control; ANOVA with Tukey’s was used. n=3–6 for each timepoint and condition.