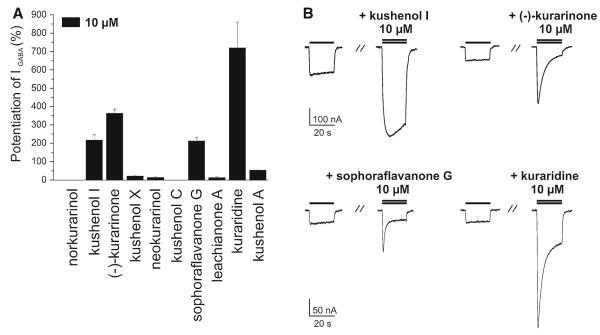
Fig. 6.
a Potentiation of IGABA through α1β2γ2S GABAA receptors by 10 μM of norkurarinol (0 ± 0%, n = 2), kushenol I (216.5 ± 29.3%, n = 5), (–)-kurarinone (362.3 ± 23.8%, n = 5), kushenol X (21.6 ± 3.4%, n = 2), neokurarinol (13.7±4.6%), n = 2), kushenol C (0±0%, n = 2, sophoraflavanone G (211.6±18.6%, n = 3), leachianone A (13.1±5.1%, n = 2), kuraridine (719.7±140.3%, n = 3), and kushenol A (53.1 ± 3.1%, n = 2). b Representative currents through α1β2γ2S GABAA receptors induced by GABA (EC3–10, single bar, control) and traces recorded during co-application of GABA (EC3–10) and the indicated compound (double bar). Current potentiation induced by the four most active compounds, kushenol I (7), (–)-kurarinone (9), sophoraflavanone G (13), and kuraridine (15) is shown