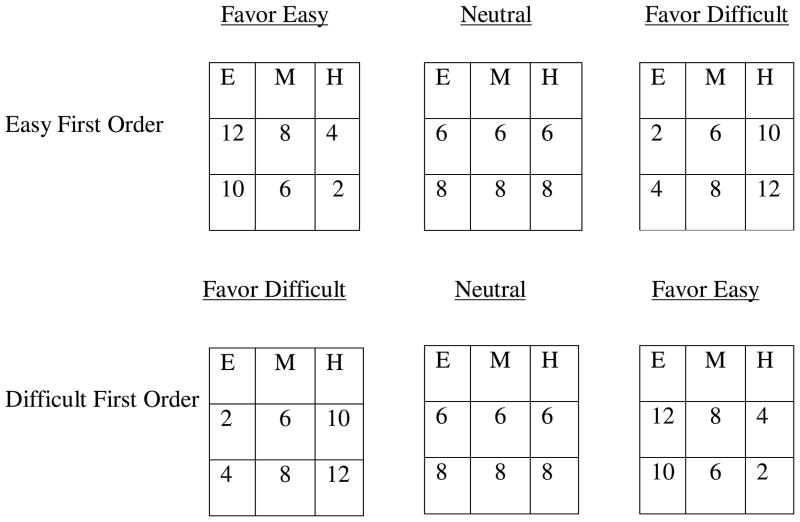
Figure 2.
Graphical depiction of the point order manipulation in which the Easy First order initially favors recall of Easy items and the Difficult First order initially favors recall of the most difficult items.
Note. Within each grid E= easy items, M= medium items, and H= difficult items; Easy First Order = the first of the three grids that participants saw for each of the four goals had points that favored recall of easy items, the second grid was neutral, and the final grid had points that favored recall of difficult items; Difficult First Order = the first of the three grids that participants saw for each of the four goals had points that favored recall of difficult items, the second grid was neutral, and the final grid had points that favored recall of the easy items.