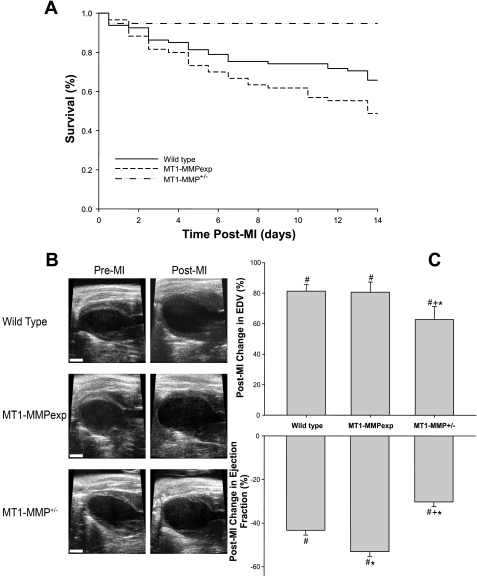
Fig. 1.
A: post-myocardial infarction (MI) 14-day survival curves for wild-type (WT) mice, cardiac-restricted overexpression of membrane type 1 matrix metalloproteinase [MT1-MMP (MT1-MMPexp)] mice, and mice heterozygous for MT1-MMP (MT1-MMP+/−). Post-MI survival was significantly lower in the MT1-MMPexp mice following MI compared with WT (P = 0.045). In marked contrast, post-MI survival was higher in the MT1-MMP+/− group compared with WT (P = 0.019) or MT1-MMPexp (P = 0.001). B: representative left ventricular (LV) long-axis echocardiographic views at end diastole before MI induction and at 14 days post-MI for the 3 groups. Significant LV dilation and posterior wall thinning at the site of the MI were readily evident in all groups (scale = 2 mm). C: changes in LV geometry as defined by end-diastolic volume (EDV) were computed on an individual basis from pre-MI values as was LV function as defined as ejection fraction. In the WT and MT1-MMPexp groups (n = 53 and 32, respectively), a significant and equivalent degree of LV dilation occurred, which was attenuated in the MT1-MMP+/− group (n = 18). LV ejection fraction fell in all groups post-MI but was lower in the MT1-MMPexp group and higher in the MT1-MMP+/− group. P < 0.05 vs. pre-MI values (#), vs. WT MI values (*), and vs. MT1-MMPexp MI values (+).