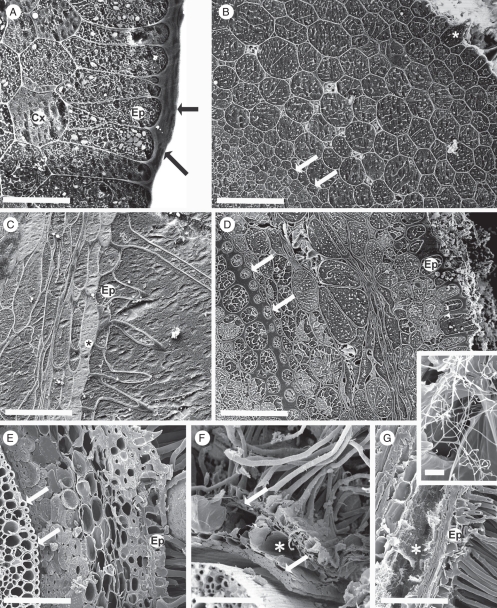
Fig. 5.
(A–D) Roots frozen in the field, cryo-planed; CSEM. (E–G) Hand-cut, frozen in the cryo-microscope. (A) 2 mm from the root tip, root hairs not yet emerged. A thick pellicle (arrows) forms the epidermal (Ep) surface, cortex (Cx) intact and thin-walled. (B) Approx. 10 mm from the tip, root hairs emerging (asterisk). The epidermal pellicle had thinned and walls of epidermis, cortex and endodermis (arrow) were thin. (C) Approx. 50 mm from the tip, a hair has developed from each epidermal cell (Ep). Vacuoles of the subepidermal layer have possible phenolic contents (asterisk). (D) Approx. 75 mm from the tip. Root hairs removed. Walls (inner tangential and radial) of endodermis (arrows) and walls (outer tangential and radial) of epidermis (Ep) had thickened. Mid-cortical cells collapsing and air spaces evident. (E) Approx. 135 mm from the tip, the cortex comprising outer and inner rims of fibres; and senescing central region. Ep, epidermis; arrows, endodermis. (F, G) Older regions, central cortex aerenchymous (asterisks), enclosed by persistent epidermis and inner and outer layers of fibres (arrows). (G) Actinobacteria in the aerenchyma (asterisk), detail in inset. Thick walls of root hairs were evident where fractured. Ep, epidermis. (C) and (G) show longitudinal faces; others are transverse. Scale bars: (A) = 35 µm; (B) = 100 µm; (C) = 80 µm; (D) = 125 µm; (E) = 150 µm; (F) = 175 µm; (G) = 150 µm; inset = 8 µm.