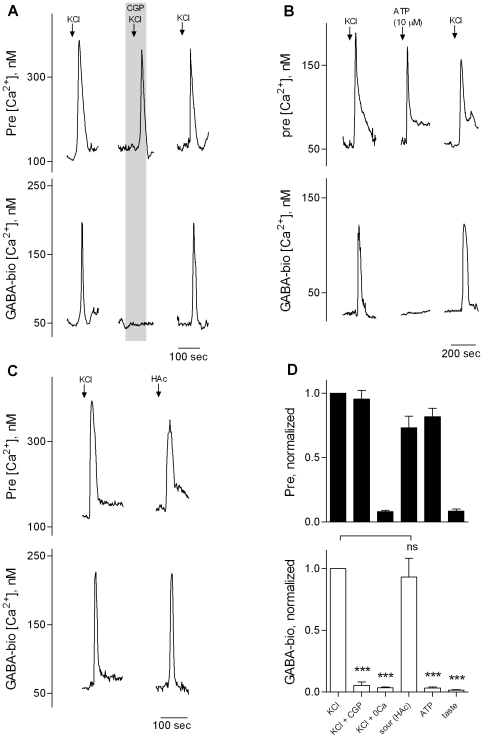
Figure 3. Stimulating Presynaptic (Type III) taste cells evokes GABA release.
GAD-GFP mice were used to isolate and identify Presynaptic taste cells. A, Traces show concurrent Ca2+ recordings from an isolated Presynaptic cell (upper traces, Pre) and an apposed GABA biosensor (lower traces, GABA-bio). Stimulating the Presynaptic cell with 50 mM KCl (↓, KCl) evoked a transient Ca2+ response and the biosensor reported that GABA was released (lower trace). CGP55845 (10 µM, “CGP”, present throughout shaded area) reversibly blocked the biosensor responses without affecting Presynaptic cell responses. B, From another experiment, KCl and ATP (10 µM) evoked Ca2+ responses in a Presynaptic cell (upper traces) but only KCl depolarization triggered GABA release (lower traces). C, Another experiment, 50 mM KCl and 10 mM acetic acid (HAc, pH 5.0) evoked a transient Ca2+ elevation in the Presynaptic cell (upper traces) and triggered GABA release (lower traces). D, Summary of data from identified Presynaptic cells. KCl depolarization (N = 4) and sour tastant (HAc, N = 4) stimulate Presynaptic cells to release GABA. CGP55845 (CGP) inhibits KCl-evoked biosensor responses. Neither tastants (sweet/bitter taste mixture, N = 3) nor ATP (N = 4) stimulates Presynaptic cells to release GABA. ns, not significant. ***, p<0.001, , Student t-test.