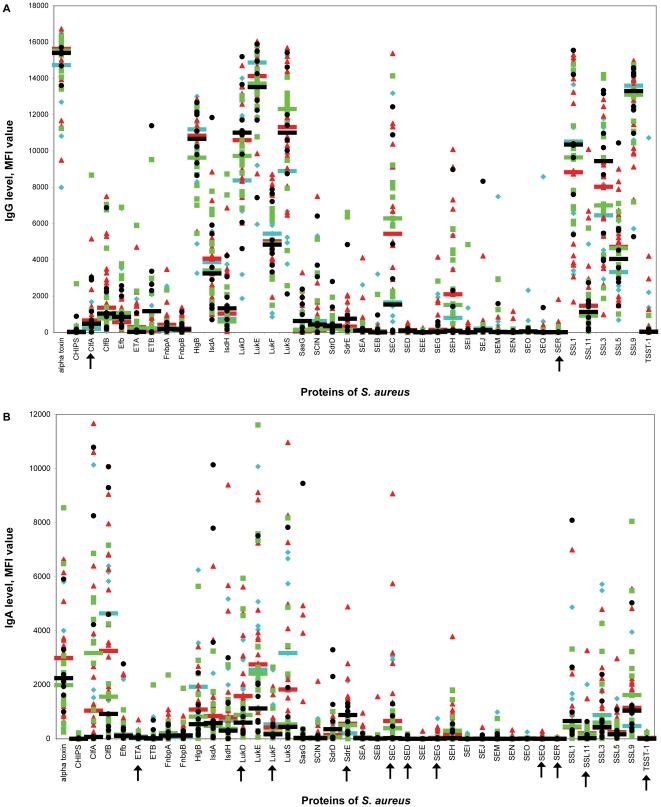
Figure 4. Relation between S. aureus nasal colonization and level of anti-staphylococcal IgG (A) and IgA (B).
Antibody levels are reflected by Median fluorescence intensity (MFI) value. Each symbol represents a single rhesus macaque. Blue diamonds represent macaques without S. aureus positive culture, red triangles represent macaques with one positive culture, green squares represent macaques with two positive cultures, and black circles represent macaques with three positive cultures. Median values are indicated by horizontal lines. Arrows indicate statistically significant differences in median values (Mann-Whitney U test). More S. aureus positive cultures were not related to high – or low – anti-staphylococcal antibody levels. CHIPS, chemotaxis inhibitory protein of S. aureus; Clf, clumping factor; Efb, extracellular fibrinogen-binding protein; ET, exfoliative toxin; Fnbp, fibronectin-binding protein; HlgB, γ hemolysin B; Isd, iron-responsive surface determinant; Luk, leukocidin; SasG, S. aureus surface protein G; SCIN, staphylococcal complement inhibitor; Sdr, serine-aspartate dipeptide repeat protein; SE, staphylococcal enterotoxin; SSL, staphylococcal superantigen-like protein; TSST-1, toxic shock syndrome toxin 1.