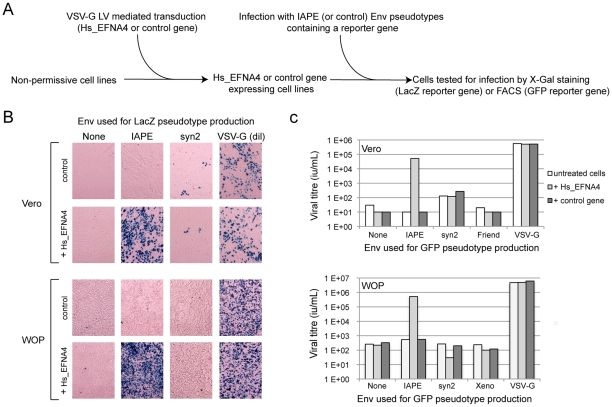
Figure 2. Expression of EFNA4 is sufficient to render cells susceptible to infection by IAPE Env pseudotypes.
Following the screening strategy presented in Figure 1, EFNA4 was identified as a potential receptor for the IAPE Env. (A) To confirm this hypothesis, its cDNA (Hs_EFNA4 for Homo sapiens EFNA4) was re-cloned in a lentiviral vector (LV) and introduced into non-permissive Vero and WOP cells that were then subjected to infection with IAPE Env pseudotypes containing either the GFP or lacZ genes. (B) For the lacZ-containing pseudotypes, the cells were fixed and stained with X-Gal to reveal ß-galactosidase activity 3 days post infection. A photo of one representative field for each condition is presented. Note than in the case of the VSV-G pseudotypes, the supernatant was diluted 200 fold before its use for infection. (C) For the GFP-containing pseudotypes, the target cells were collected 3 days post infection and subjected to FACS analysis in order to quantify the proportion of GFP-positive cells, allowing precise calculation of the viral titres (see Methods for details). The results presented in B and C correspond to one representative experiment out of 3.