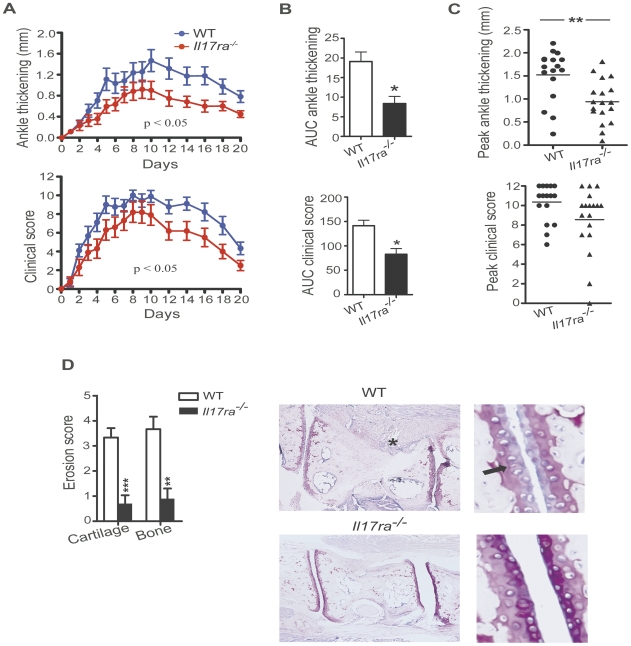
Figure 1. IL-17RA deficiency attenuates severity of K/BxN serum induced arthritis.
A, WT (n = 9) and Il17ra−/− mice (n = 10) were injected with K/BxN serum and were monitored for 20 days recording daily ankle thickness and clinical score. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. The AUC for the ankle thickness and for the clinical score of every individual mouse was calculated and statistical differences between wild-type and Il17ra−/− mice were determined by unpaired two-tailed Student's t test. One representative of three independent experiments is shown. The number of mice stated above refers to this one representative experiment. B, AUCs for the ankle thickness and the clinical score of WT (n = 17) and Il17ra−/− mice (n = 18) were calculated. Each column represents mean ± SEM. Data were pooled from three independent experiments, and statistical differences were determined by unpaired two-tailed Student's t test. C, Peak ankle thickness and the peak clinical score reached by each WT (•) (n = 17) and Il17ra−/− (▴) mice (n = 18) are shown. Each dot or triangle represents one individual mouse. Data were pooled from three independently performed experiments. D, Histopathological score of cartilage and bone erosions in WT (n = 9) and Il17ra−/− mice (n = 10) are presented as mean ± SEM from ankles harvested on day 21. Data shown are from one representative out of three independently performed experiments. Histopathological score was assessed in toluidine-blue stained specimens. Representative histologies for the wild-type and Il17ra−/− groups are shown. The asterisk marks a site of pannus infiltration into the bone already visible under low magnification. The arrow indicates a site of proteoglycan loss of the cartilage. Both findings were typical for the wild-type group but not for the Il17ra−/− group. In (C) and (D) statistical analyses were conducted using Mann-Whitney-Wilcoxon test. * = p<0.05; ** = p<0.01; *** = p<0.001.