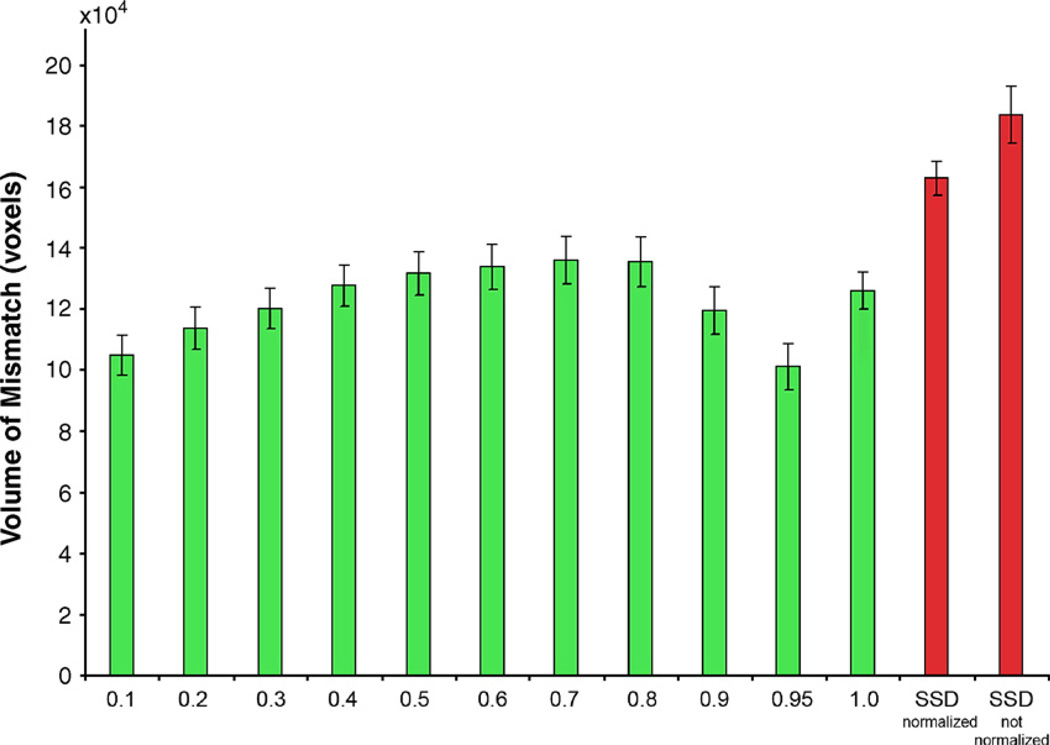
Fig. 3.
The volume of mismatch between the registered source and target brain MR images for different values of α in the cost functional (Jensen–Rényi divergence; green bars) used to align the images. α=1 represents the mutual information. The volume of mismatch based on minimizing the summed squared intensity differences (SSD; red bars) is plotted for reference (SSD is a simpler cost functional, often used in linear and nonlinear image registration, see, e.g., Woods et al., 1998; Ashburner and Friston, 1999 for examples in brain mapping). To allow better registration performance using SSD, prior to image deformation, intensities in the two images were scaled (i.e., intensity normalized) such that the mean intensities over the brain were the same. Although the registration accuracy based on SSD is improved after the image intensities are normalized, the performance of JRD in the 3D experiments is still better than that of SSD, at least on this dataset.